Engine Isx15 Cummins Cummins Isx Serpentine Belt Diagram
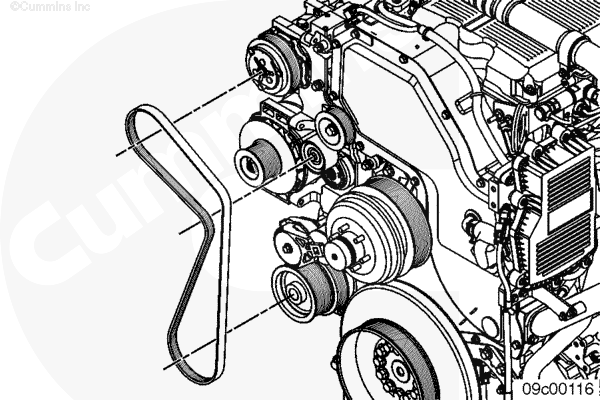
Alright, let's dive into the serpentine belt system on your Cummins ISX15. This guide isn't just about replacing a worn belt; it's about understanding the whole system so you can diagnose problems, perform preventative maintenance, and even make informed decisions when modifying your engine. We'll focus heavily on the serpentine belt diagram, because understanding it is the key to everything else. Think of this as your comprehensive reference guide.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why bother with a diagram at all? Well, the serpentine belt in your ISX15 drives several critical engine components. A broken or improperly routed belt can lead to catastrophic engine failure. The diagram serves several vital purposes:
- Repair and Replacement: The most obvious reason. When the belt snaps or shows signs of wear (cracks, fraying, glazing), the diagram ensures you route the new belt correctly. Incorrect routing can damage components and prevent them from working.
- Troubleshooting: A squealing belt? The diagram helps you identify which component might be the source of the problem (e.g., a failing idler pulley or a seizing A/C compressor).
- Preventative Maintenance: Knowing the system layout allows you to visually inspect all components for damage, leaks, or misalignment, catching potential problems before they become major headaches.
- Modification and Upgrades: Planning to install a higher-output alternator or a different A/C compressor? Understanding the belt routing and tensioning is crucial for ensuring proper fitment and operation.
- Learning: Even if you don’t intend to work on your engine yourself, knowing how the serpentine belt system functions gives you a deeper understanding of your ISX15.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we get into the diagram itself, let's identify the major components involved. The ISX15 serpentine belt system typically includes:
- Crankshaft Pulley (Damper): The driven pulley, provides the rotational force for the belt, connected directly to the crankshaft.
- Alternator: Generates electricity to power the vehicle's electrical system.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor: Compresses refrigerant for the A/C system.
- Power Steering Pump: Provides hydraulic pressure for power steering.
- Idler Pulleys: Smooth, bearing-mounted pulleys that guide the belt around other components. Often used to change the belt’s angle of approach to a drive pulley.
- Tensioner Pulley: An automatically adjusted pulley that applies the correct tension to the serpentine belt. This is critical for proper operation and belt life. Usually spring-loaded.
Key Specs: While the specific belt length varies depending on the ISX15's configuration (e.g., with or without A/C, different alternator sizes), you'll typically find the belt length printed directly on the belt itself. If replacing, always use a belt with the exact specified length. The tensioner pulley has a specific operating range marked on it. The tensioner position needs to be within this range when the new belt is installed. Consult your specific ISX15 engine's service manual for the precise belt length and tensioner range.
Understanding the Serpentine Belt Diagram: Symbols and Conventions
The diagram isn't just a random drawing of pulleys and a belt. It uses specific conventions to convey information clearly:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent the path of the serpentine belt itself.
- Dashed Lines: May indicate the location of components behind other components, or the direction of belt travel.
- Arrows: Show the direction of rotation for each pulley. This is crucial for understanding how the belt drives each component.
- Symbols for Components: Each component is represented by a simplified drawing. Alternators usually have a symbol resembling a generator, water pumps are depicted with a circular shape and vanes inside, and so on.
- Tensioner Markings: The tensioner pulley will have markings indicating the acceptable operating range. The diagram might highlight this range to ensure proper belt installation.
Furthermore, some diagrams may employ color coding. For example, different colors might be used to distinguish between the "smooth" (back) side of the belt and the "grooved" (ribbed) side, which engages with the pulleys.
Important Note: Not all diagrams are created equal. Some are highly detailed, while others are more schematic. Learn how to read the specific diagram you are using!
How It Works: The Serpentine Belt System in Action
The serpentine belt system is elegantly simple in concept. The crankshaft pulley, driven by the engine's rotation, powers the entire system. The belt wraps around each of the other pulleys, transferring rotational force. The tensioner pulley maintains the proper tension, preventing slippage and ensuring efficient power transfer. If the belt is too loose, it will slip, causing noise and reduced performance of the driven components. If the belt is too tight, it can overload the bearings in the components and cause premature failure. The key is to have the correct tension.
The routing of the belt is critical. The belt must wrap around each pulley in the correct direction and with the correct amount of contact. This ensures that each component receives the necessary power to operate properly. The tensioner is a pivotal part. As the belt stretches over time, the tensioner automatically adjusts to maintain the proper tension. It is important to inspect the tensioner for wear, proper operation, and adequate dampening (if equipped). A failing tensioner can cause belt slippage, noise, and even premature belt failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how you can use your knowledge of the serpentine belt system and the diagram to diagnose common problems:
- Squealing Belt: This is often caused by a loose belt, a glazed belt (where the belt becomes smooth and hard), or a failing pulley bearing. Use the diagram to identify the pulleys and check them for smooth rotation. If the belt is loose, inspect the tensioner.
- Belt Slippage: This can manifest as dimming headlights or a lack of A/C performance. Again, check the belt tension and the condition of the belt and pulleys. Look for signs of oil or coolant contamination on the belt, as this can cause slippage.
- Premature Belt Failure: This could be caused by misaligned pulleys, a failing tensioner, or a worn or damaged pulley. Use a straightedge to check the alignment of the pulleys. A severely misaligned pulley will rapidly wear out a belt.
- Component Failure: If the alternator, water pump, or A/C compressor fails, it can put excessive stress on the belt, causing it to break. Diagnose and repair the failing component before replacing the belt.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some key safety points:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any part of the electrical system, disconnect the negative battery cable. This will prevent accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Engine Off and Cool: Never work on the serpentine belt system while the engine is running or hot. Serious injury or burns can occur.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands, tools, and clothing away from moving parts. The serpentine belt can cause serious injury if it catches on something.
- Tensioner Safety: The tensioner pulley is under spring pressure. When releasing the tension, be careful to control the tensioner to prevent it from snapping back and causing injury. Always use the correct tool to relieve the tension.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The crankshaft pulley is a heavy component attached to the engine, and it's constantly spinning when the engine is running. Under no circumstances should you attempt to stop the rotation of the crankshaft pulley by hand or with any tool. This could result in serious injury. Also, remember that many of the components driven by the serpentine belt, like the alternator and water pump, are electrically and hydraulically connected, respectively. Take care when handling these parts, especially if you are not experienced with automotive repair.
We have the Cummins ISX15 Serpentine Belt Diagram available for download. This diagram will serve as a valuable reference guide for your repairs and maintenance. Please use it responsibly and always prioritize safety.
