Español 300 Chrysler Diagrama De Fusibles Chrysler 300c 2006
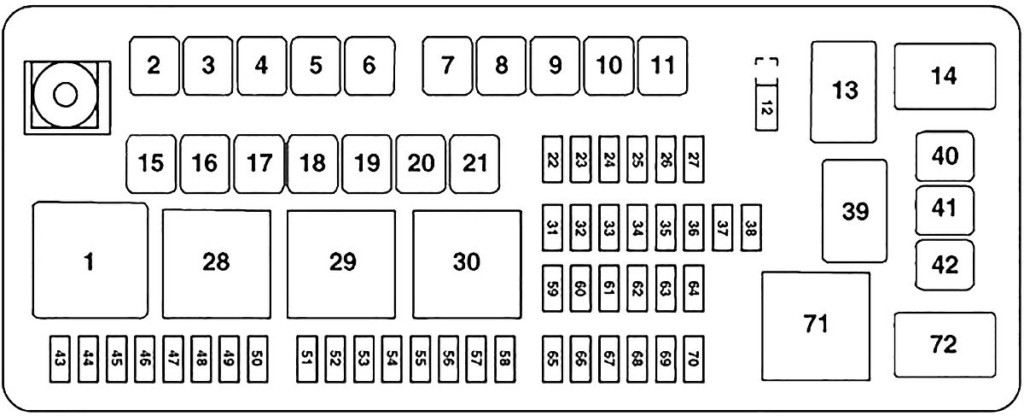
Alright, let's dive into the world of Chrysler 300C (2006) fuse diagrams – specifically, focusing on what some might refer to as the "Español 300 Chrysler Diagrama De Fusibles Chrysler 300c 2006". While that specific phrasing might seem a little redundant, the core concept remains crucial for anyone tackling electrical repairs or modifications on this iconic car. This guide aims to be your comprehensive resource. We'll break down the diagram's elements, explain how it functions, and offer practical troubleshooting advice. Plus, good news – we have the complete fuse diagram file available for you to download, giving you an invaluable resource at your fingertips!
Purpose of the Fuse Diagram
Why is this diagram so essential? The Chrysler 300C, especially the 2006 model, has a complex electrical system. Fuses act as safety nets, protecting sensitive components from overcurrent situations. Think of them like miniature circuit breakers. If a circuit draws too much current – perhaps due to a short circuit, a malfunctioning component, or an overload – the fuse will blow, breaking the circuit and preventing further damage.
The fuse diagram is your roadmap to understanding this protective system. It allows you to quickly identify which fuse corresponds to which circuit. This is crucial for:
- Troubleshooting electrical problems: When a component stops working (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows), the fuse is often the first place to check.
- Performing modifications: Adding aftermarket accessories requires you to tap into existing circuits or create new ones. The fuse diagram helps you choose appropriate connection points and fuse ratings.
- Understanding your vehicle's electrical system: Simply knowing the layout and function of the fuses provides a better understanding of how your car operates.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Fuse System
The Chrysler 300C (2006) typically features two main fuse locations:
- Power Distribution Center (PDC): Located under the hood, usually near the battery. This houses larger fuses and relays responsible for protecting high-current circuits like the starter motor, alternator, and major engine management systems.
- Interior Fuse Block: Usually located inside the cabin, often on the driver's side, behind a panel or under the dashboard. This protects lower-current circuits such as the radio, lights, power windows, and other interior accessories.
Each location contains a variety of fuses, each rated for a specific amperage (A). Common amperage ratings include 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and higher. The amperage rating indicates the maximum current the fuse can handle before blowing. Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage is extremely dangerous and can cause serious damage or even a fire. Always use the correct amperage rating as specified in the diagram.
The fuse diagram itself will list each fuse location, its amperage rating, and the circuit it protects. It might also include the corresponding relay information, although relays are less frequently replaced than fuses.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Fuse diagrams utilize a standard set of symbols to convey information efficiently. Understanding these symbols is critical for accurate interpretation.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical circuits or wiring. Thicker lines usually indicate higher-current circuits.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated next to the circuit lines, allowing you to trace wires within the vehicle. Common colors include red, black, blue, green, yellow, and white, often with stripes (e.g., red/white). These colors are often abbreviated, like "RD" for Red, "BK" for Black, and so on. Understanding these abbreviations is key to following the diagram.
- Icons: Icons represent the components protected by the fuse. For example, a headlight icon will indicate the fuse protecting the headlight circuit. Common icons include lights, motors, radios, windows, and engine-related components. These icons are generally intuitive, but a key legend on the diagram will spell out their specific meanings.
- Fuse Symbol: The symbol for a fuse is usually a zigzag line inside a rectangle.
- Relay Symbol: The symbol for a relay is usually a coil with a switch.
The diagrams are often laid out in a hierarchical fashion, showing how power flows from the battery, through the fuse, and to the component. Pay close attention to the ground symbol (often a series of horizontal lines), which indicates the return path for the electrical current.
How It Works: The Electrical Circuit and Fuse Protection
The fuse diagram illustrates a series of parallel and serial circuits. Each fuse protects a specific branch of the electrical system. When an electrical device (e.g., a light bulb) is switched on, current flows from the battery, through the fuse, through the switch, through the load (the bulb), and back to the battery through the ground. If the circuit is properly designed, the current flow will be within the fuse's rated amperage.
However, if a short circuit occurs (e.g., a wire chafes and touches the chassis), the resistance of the circuit drops dramatically, and the current flow increases exponentially. This surge of current causes the fuse element (a thin strip of metal inside the fuse) to heat up rapidly and melt, breaking the circuit and stopping the current flow. This prevents the short circuit from damaging other components or starting a fire. The fuse is a sacrificial element designed to protect the rest of the system.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say your power windows stop working. Here's how you'd use the fuse diagram:
- Consult the Fuse Diagram: Locate the interior fuse block diagram (either in your owner's manual or the downloadable file we provide).
- Identify the Power Window Fuse: Find the fuse labeled "Power Windows" or something similar. The diagram will specify the fuse's location within the fuse block and its amperage rating.
- Inspect the Fuse: Remove the fuse using a fuse puller (a small plastic tool designed for this purpose). Visually inspect the fuse. If the thin metal strip inside the fuse is broken, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Circuit: Turn on the power windows to see if they now function.
If the fuse blows again immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the power window circuit. This requires further investigation, potentially involving checking the wiring, the window motor, and the window switch. Do not simply replace the fuse with a higher amperage fuse. This is a recipe for disaster!
Another common scenario: an aftermarket radio install. The fuse diagram is critical for identifying a suitable power source and ensuring you're not overloading an existing circuit. Always use a fuse tap or add a dedicated circuit with its own fuse to protect your new radio and the car's electrical system.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems involves inherent risks. Always observe these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative battery cable. This prevents accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Use Appropriate Tools: Use insulated tools designed for automotive electrical work.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This eliminates the circuit's protection and can lead to a fire.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: If you're soldering or using electrical cleaners, work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful fumes.
- High-Current Circuits: Be extremely cautious when working with high-current circuits, such as the starter motor and alternator circuits. These can deliver a dangerous electrical shock.
Remember the PDC under the hood houses circuits that, if mishandled, can be very dangerous. Components connected to the ignition system, fuel injection, and emissions control are all vital for proper engine operation. Incorrect alterations can cause significant problems, including driveability issues or even engine damage.
Always double-check the fuse diagram and consult with a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any aspect of the electrical system.
With the Chrysler 300C (2006) fuse diagram in hand and a clear understanding of its principles, you'll be well-equipped to diagnose and resolve electrical issues, perform modifications safely, and maintain your vehicle's electrical system effectively. Remember to exercise caution, follow best practices, and never hesitate to seek professional help when needed.
Ready to get your hands on the diagram? You can download the complete "Español 300 Chrysler Diagrama De Fusibles Chrysler 300c 2006" file – and potentially multiple versions for different trim levels – from us. This will be an indispensable tool in your automotive endeavors.
