Ford Brake Controller Wiring Diagram
So, you're thinking about tackling your Ford's brake controller wiring, eh? Smart move. Understanding this system is crucial, whether you're installing a new controller, troubleshooting trailer braking issues, or just deepening your automotive knowledge. This article will break down the Ford brake controller wiring diagram, making it understandable and actionable for experienced DIYers like yourself. We'll cover everything from the diagram's purpose to real-world troubleshooting tips, all while emphasizing safety.
Purpose of the Brake Controller Wiring Diagram
Let's start with why you'd even need this diagram. A brake controller wiring diagram serves as the blueprint for your trailer's braking system's electrical connections within your Ford. Its primary purposes are:
- Installation: Essential for safely and correctly installing an aftermarket brake controller.
- Troubleshooting: Helps diagnose electrical problems causing weak, intermittent, or non-existent trailer braking.
- Repair: Guides you in repairing damaged wiring or connectors within the brake controller circuit.
- Modification: If you're customizing your towing setup, understanding the wiring is paramount.
- Education: Just plain learning how the system functions – empowering you to be a more capable vehicle owner.
Without the diagram, you're essentially guessing. That's a recipe for disaster, potentially damaging your vehicle's electrical system or creating a serious safety hazard on the road.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before diving into the diagram itself, let's define the key components involved. A Ford brake controller wiring system typically includes the following elements:
- Brake Controller Unit: The brains of the operation, applying proportional braking force to the trailer brakes. This typically has adjustments for gain and braking type.
- Vehicle Battery: Provides the necessary power for the entire trailer braking system. Often, a dedicated, high-amperage circuit is used.
- Brake Pedal Switch: This switch activates when you press the brake pedal, sending a signal to the brake controller.
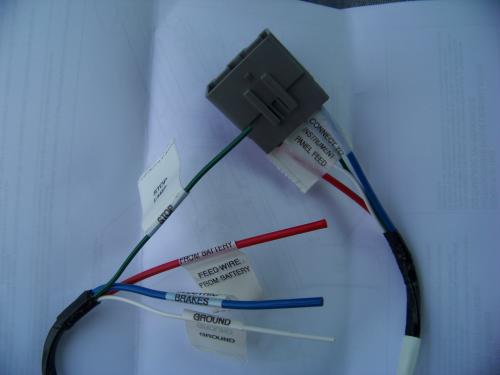
- Trailer Connector (Typically 7-way): The interface between your Ford and the trailer. Standard 7-way connectors include circuits for trailer lights, ground, auxiliary power, and, most importantly, the brake signal.
- Wiring Harness: The network of wires connecting all the components. Ford wiring harnesses are often color-coded, but variations can exist between model years.
- Fuses and Relays: Safety devices that protect the electrical system from overloads and control the flow of current.
The specifications you'll want to pay attention to on the diagram include wire gauge (thickness), fuse ratings, and voltage levels. Using the correct wire gauge is crucial for carrying the required current without overheating and potentially causing a fire.
Understanding the Wiring Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
Now for the heart of the matter: deciphering the diagram itself. Here's a breakdown of common symbols and conventions:
- Lines: Represent wires. Thicker lines often indicate wires carrying higher current.
- Colors: Crucial for identifying wires in the real world. Ford typically uses a color-coding scheme (e.g., blue for brake output, white for ground). However, always verify wire colors with a multimeter before making any connections, as variations can occur, especially in older vehicles or after previous repairs.
- Symbols:
- Battery: Represented by a series of short and long parallel lines.
- Ground: Typically depicted as a downward-pointing triangle or a series of stacked lines decreasing in size. A good ground is essential for proper brake controller operation.
- Fuse: Usually a zig-zag line within a rectangular box. The diagram will often indicate the fuse's amperage rating (e.g., 20A).
- Relay: Shown as a coil and a switch. The coil, when energized, closes the switch, allowing current to flow to the brake controller.
- Brake Switch: Depicted as a mechanical switch that closes when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Connector: Represented by interlocking symbols, showing how the wires connect. These connectors often have pin numbers that correspond to the wiring diagram.
- Wire Gauge: Often noted on the diagram next to the wire line, indicating the wire's thickness (e.g., 12 AWG, 14 AWG). Lower numbers indicate thicker wires.
Important Note: Ford brake controller wiring diagrams can vary depending on the model year, trim level, and specific options installed on your vehicle. Always use the diagram specifically designed for your Ford. We have a library of diagrams available, and the link for your specific model is available to download at the end of this article.
How It Works: A Step-by-Step Overview
Let's trace the typical electrical flow in a Ford brake controller system:
- Power Supply: The brake controller receives power directly from the vehicle's battery, typically through a dedicated circuit protected by a fuse.
- Brake Pedal Activation: When you press the brake pedal, the brake pedal switch closes, sending a signal (usually +12V) to the brake controller.
- Controller Processing: The brake controller receives the signal from the brake switch and, based on the gain setting and the vehicle's deceleration rate (if equipped with inertial sensing), determines the appropriate amount of braking force to apply to the trailer brakes.
- Output to Trailer: The brake controller sends a variable voltage signal (typically 0-12V) through the blue wire (typically) to the trailer connector's brake output pin.
- Trailer Braking: This voltage signal activates the electromagnets in the trailer brakes, applying braking force to the trailer wheels.
- Ground: All electrical components require a solid ground connection to function correctly. The trailer connector and brake controller will have dedicated ground wires connected to the vehicle's chassis.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Okay, time to put this knowledge to practical use. Here are some common troubleshooting scenarios and how the wiring diagram can help:
- No Trailer Brakes:
- Check the fuses: Use the diagram to locate the fuse(s) for the brake controller circuit and trailer brakes. Replace any blown fuses with the correct amperage rating.
- Verify Ground Connection: A poor ground is a common culprit. Inspect the ground wires for corrosion or loose connections. Use a multimeter to verify continuity between the ground wire and the vehicle chassis.
- Test the Brake Pedal Switch: Use a multimeter to check if the brake pedal switch is sending a signal when the pedal is pressed.
- Check the Trailer Connector: Inspect the trailer connector for damaged pins or corrosion. Use a test light or multimeter to verify that the brake output pin is receiving voltage when the brake pedal is pressed.
- Controller Malfunction: If all wiring checks out, the brake controller itself might be faulty.
- Weak Trailer Brakes:
- Gain Adjustment: Make sure the gain setting on the brake controller is properly adjusted for the trailer weight.
- Voltage Drop: Excessive voltage drop in the wiring can reduce braking force. Check the voltage at the trailer connector's brake output pin while applying the brakes. A significant drop indicates a wiring problem (corrosion, undersized wires).
- Intermittent Trailer Brakes:
- Loose Connections: Check all wiring connections for looseness or corrosion. Pay particular attention to connectors and ground points.
- Wiring Damage: Inspect the wiring harness for any signs of damage (frayed wires, cuts, or abrasions).
Safety: Respect the Electrical System
Electrical systems can be dangerous. Always disconnect the negative terminal of the vehicle's battery before working on the brake controller wiring. This prevents accidental shorts and potential electrical shocks. Fuses are there for a reason! Never replace a fuse with a higher amperage rating. This could overload the circuit and cause a fire. When working near airbags or other safety systems, follow all manufacturer's instructions to avoid accidental deployment. Be especially careful when dealing with components near the firewall. There's often a concentration of wiring and sensitive components there.
Always double-check your work. Use a multimeter to verify continuity and voltage levels before reconnecting the battery. A mistake in the wiring can damage the brake controller, the vehicle's electrical system, or, most importantly, cause a brake failure on the road.
With a little patience and the right information, you can confidently tackle your Ford brake controller wiring. Remember to always prioritize safety, use the correct tools, and consult the wiring diagram for your specific vehicle. Good luck!
We have the full wiring diagram available for download. Click here to download the specific diagram for your Ford model.
