Ford Ignition Switch Wiring Color Code
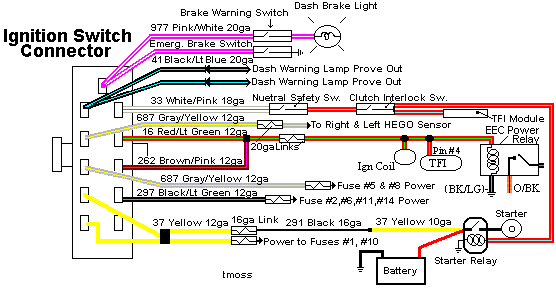
Understanding the Ford ignition switch wiring color code is crucial for a variety of automotive tasks, from basic repairs and troubleshooting to more advanced modifications and security system installations. A clear grasp of these color codes allows you to diagnose electrical issues more effectively, avoid costly mistakes, and even enhance your vehicle's functionality. This article will provide you with an in-depth look at the Ford ignition switch wiring system, its components, and how to interpret the wiring diagrams that are essential for working with it.
Purpose: Why Understanding Ignition Switch Wiring Matters
Why should you bother learning about ignition switch wiring? Several reasons stand out:
- Repairing a Faulty Switch: Ignition switches fail. Knowing the wiring allows you to test individual circuits, pinpoint the problem (e.g., a broken wire, a short circuit), and replace or repair the switch correctly.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding remote starters, alarms, or other electrical accessories often requires tapping into the ignition system. Correct wiring is *critical* to avoid damaging your vehicle's electrical system.
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: When your car won't start, or exhibits strange electrical behavior, the ignition switch is a prime suspect. Understanding the wiring allows for methodical testing.
- Modifying Your Vehicle: Performance upgrades or custom builds may necessitate altering the ignition system. Knowing the wiring beforehand prevents costly errors.
- Security Enhancements: Understanding the ignition wiring enables you to install kill switches or other anti-theft devices that interrupt key circuits.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The ignition switch is a multi-position rotary switch that controls the flow of electrical power to various circuits within your vehicle. It typically has several positions:
- LOCK: The steering wheel is locked, and the ignition is off. Power is typically cut to most circuits.
- ACC (Accessory): Power is supplied to accessories like the radio and climate control, but not to the engine ignition system.
- ON (Run): The engine control unit (ECU), fuel pump, and other essential systems receive power. This is the normal operating position when the engine is running.
- START: The starter motor is engaged to crank the engine.
The ignition switch itself is connected to the vehicle's wiring harness via a connector. This connector contains several terminals, each corresponding to a different circuit. Key components connected to the ignition switch include:
- Battery (B+): Supplies direct power from the battery. This is the primary power source for the switch.
- Ground: Provides a return path for electrical current.
- Ignition (IGN): Supplies power to the ignition system and ECU when the switch is in the ON or START positions.
- Accessory (ACC): Supplies power to accessories like the radio and climate control when the switch is in the ACC or ON positions.
- Starter (ST): Supplies power to the starter solenoid when the switch is in the START position.
Ford's wiring color codes are generally consistent, but they can vary slightly depending on the vehicle model and year. Therefore, always consult the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle. Common wire colors include:
- Red: Typically used for battery power (B+).
- Black: Typically used for ground.
- Yellow: Often used for starter circuits.
- Brown: Commonly used for accessory circuits.
- Green: Can be used for various circuits, often related to lights or signals. Always verify the exact function.
- Blue: Similar to green, may be used for various functions, requiring diagram verification.
Symbols: Understanding Wiring Diagrams
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Represent wires. Solid lines indicate direct connections, while dashed lines may indicate connections through a relay or other component. Thicker lines often denote wires carrying higher current loads.
- Colors: Indicated using abbreviations or full color names (e.g., RD for Red, BLK for Black, YEL for Yellow).
- Circles: May represent terminals, connectors, or splices.
- Rectangles: Typically represent components like relays, fuses, or modules.
- Switches: Depicted as a line connecting to one or more other lines, showing the path of current flow when the switch is closed. The ignition switch, in a diagram, will have multiple positions shown.
- Ground Symbol: Usually a series of downward-pointing lines or a triangle connected to a horizontal line.
- Fuse Symbol: Looks like a squiggly line inside a rectangle or bracket.
Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting wiring diagrams accurately. When tracing a circuit, follow the lines, noting the color codes and the components they connect to. A voltmeter is your best friend for verifying the presence of voltage on each line according to its function.
How It Works: The Flow of Electricity
When you turn the ignition key, you're essentially closing circuits within the ignition switch, directing power to different components in a specific sequence.
- LOCK: No circuits are closed except perhaps a low-power circuit for key-in-ignition chime or immobilizer system.
- ACC: The switch closes the circuit that provides power to the accessory terminal. This activates the radio, climate control, and other non-essential accessories.
- ON: The switch closes the circuits that provide power to both the accessory and ignition terminals. The ignition terminal powers the ECU, fuel pump, ignition coils, and other systems necessary for engine operation.
- START: In addition to the ACC and IGN circuits, the switch closes the circuit that provides power to the starter solenoid. This engages the starter motor, which cranks the engine. Once the engine starts, you release the key, and the switch returns to the ON position.
The ignition switch acts as a gatekeeper, controlling the flow of power based on the key position. It is a relatively simple mechanical device with significant electrical consequences.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few troubleshooting tips when working with the Ford ignition switch wiring:
- No Start: If the engine won't crank, check the starter circuit (usually yellow). Use a test light or multimeter to verify that power is reaching the starter solenoid when the key is in the START position. Check the fuse for the starter circuit. A blown fuse is a common culprit.
- No Accessory Power: If accessories aren't working in the ACC position, check the accessory circuit (often brown). Verify that power is reaching the accessory terminal when the key is in the ACC or ON positions. Check the fuse associated with the accessories.
- Engine Dies After Starting: This could be an issue with the ignition circuit. The starter circuit may be working, but the ignition circuit isn't taking over when the key returns to the ON position. Verify power to the ignition terminal.
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter is essential for testing voltage and continuity. Test for voltage between the terminal and ground. Test for continuity (zero resistance) on ground wires.
Always consult the vehicle's wiring diagram before attempting any repairs. Make sure you have identified the correct wire *before* cutting or splicing it. A mistake can lead to serious electrical damage.
Safety: Highlighting Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems involves inherent risks. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical component, disconnect the negative battery cable. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Batteries can produce hydrogen gas, which is flammable. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid the risk of explosion.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to protect yourself from electrical shock.
- Be Careful with Airbags: Some airbag systems are connected to the ignition switch. Disconnecting the battery *may not* be enough to disable the airbag system. Consult the vehicle's service manual for proper airbag disabling procedures *before* working on the ignition switch. Improper handling of airbag systems can result in serious injury.
- Be mindful of the CAN bus. The Controller Area Network (CAN) bus is a communication network that allows various electronic control units (ECUs) in a vehicle to communicate with each other. Modern Ford vehicles rely heavily on the CAN bus. Incorrect wiring modifications can disrupt the CAN bus communication, leading to a variety of problems, including engine stalling, ABS failure, and airbag deployment issues. Before making any modifications, consult the vehicle's wiring diagram and be aware of the CAN bus wiring.
The ignition switch itself can be a high-current component, especially the starter circuit. Shorts in this circuit can lead to fires. Always ensure that wiring is properly insulated and that fuses are correctly sized.
With a basic understanding of Ford ignition switch wiring diagrams and wiring color codes, you're well-equipped to handle a variety of automotive tasks. Remember to always consult your vehicle's specific wiring diagram and prioritize safety.
We have a comprehensive Ford ignition switch wiring diagram file available for download to aid in your troubleshooting and repair endeavors. Please contact us to obtain the file and ensure you have the right resources at your disposal.
