Four Wheeler Atv Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
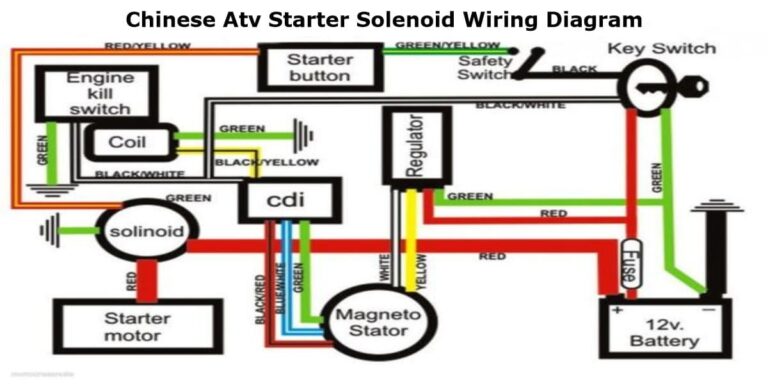
Hey there, fellow gearheads! Let's dive into the often-overlooked but crucial component of your four-wheeler or ATV's starting system: the starter solenoid. This article will walk you through understanding its wiring diagram, empowering you to diagnose issues, perform repairs, or even customize your ride. Whether you're troubleshooting a no-start condition or just expanding your mechanical knowledge, grasping the solenoid's wiring is essential. We'll break down the technical jargon into plain language, so you can confidently tackle any electrical challenge your ATV throws your way.
Why Understanding the Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram Matters
Knowing your ATV's starter solenoid wiring is crucial for several reasons:
- Troubleshooting No-Start Conditions: A faulty solenoid is a common cause of a machine that won't crank. Understanding the wiring diagram allows you to pinpoint the problem, ruling out other potential culprits like the battery, starter motor, or ignition switch.
- Performing Repairs: Replacing a faulty solenoid is often straightforward, but correct wiring is paramount. Miswiring can damage the solenoid, starter motor, or other electrical components.
- Customization and Modification: If you're adding aftermarket accessories or modifying your ATV's electrical system, understanding the starter solenoid's wiring is essential to avoid conflicts and ensure proper operation.
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly inspecting the wiring and connections can help you identify potential problems before they lead to a breakdown.
- Expanding Your Knowledge: Gaining a solid understanding of basic automotive electrical systems, like the one used for the starter, is always a good idea. This applies to cars, motorcycles, and many other kinds of vehicles!
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Starter Solenoid System
Before we delve into the wiring diagram, let's familiarize ourselves with the key components and specifications of a typical ATV starter solenoid system:
- Battery: The heart of the electrical system, providing the necessary power (typically 12V DC) to crank the engine.
- Ignition Switch: This switch is responsible for activating the electrical circuits required to start the ATV. When you turn the key, it sends a signal to the starter solenoid.
- Starter Solenoid: An electromagnetic switch that acts as a relay, delivering high current from the battery to the starter motor. It allows a low-current circuit (from the ignition switch) to control a high-current circuit (to the starter motor). Inside, a coil of wire creates a magnetic field when energized, pulling a plunger that closes heavy-duty contacts.
- Starter Motor: An electric motor that engages with the engine's flywheel or flexplate to crank the engine.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connects all the electrical components.
- Fuse(s): Protect the electrical system from overcurrent and short circuits.
- Ground Connection(s): Provides a return path for the electrical current to the battery. A good ground is essential for proper operation.
Key Specifications:
- Voltage: Typically 12V DC.
- Amperage: The solenoid must be rated to handle the high amperage draw of the starter motor. Ratings typically range from 100A to 300A or more.
- Coil Resistance: The resistance of the solenoid's coil, which affects the current draw from the ignition switch circuit.
Understanding Wiring Diagram Symbols
Wiring diagrams use standardized symbols to represent electrical components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common symbols you'll encounter in a starter solenoid wiring diagram:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line may indicate the wire gauge (thicker lines = larger gauge = higher current capacity).
- Dashed Lines: Often represent a ground connection or a shielded wire.
- Circles: Can represent various components, depending on what's inside.
- Rectangles: Often represent switches, relays, or fuses.
- Zigzag Lines: Represent resistors or coils (like the solenoid coil).
- Ground Symbol (often three horizontal lines decreasing in size): Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Battery Symbol (alternating long and short lines): Represents the battery.
Wire Colors: Wiring diagrams often use color codes to identify individual wires. Common color codes include:
- Red: Typically used for positive (+) battery connections.
- Black: Typically used for ground (-) connections.
- Yellow, Blue, Green, Brown: Used for various other circuits, depending on the manufacturer. Always refer to the specific wiring diagram for your ATV model.
How the Starter Solenoid System Works
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how the starter solenoid system works:
- Turning the Ignition Key: When you turn the ignition key to the "Start" position, it completes a low-current circuit that energizes the starter solenoid's coil.
- Solenoid Activation: The energized coil creates a magnetic field, pulling a plunger inside the solenoid.
- Contact Closure: The plunger movement closes heavy-duty electrical contacts within the solenoid. These contacts connect the battery's positive (+) terminal directly to the starter motor.
- Starter Motor Activation: The high current from the battery flows through the closed contacts to the starter motor, causing it to spin.
- Engine Cranking: The starter motor's spinning action engages with the engine's flywheel (or flexplate), cranking the engine until it starts.
- Releasing the Ignition Key: When you release the ignition key, the low-current circuit to the solenoid is broken. The magnetic field collapses, the plunger retracts, and the contacts open, disconnecting the battery from the starter motor.
Essentially, the solenoid acts as a powerful remote switch. It allows you to use a small current from the ignition switch to control a large current that’s needed by the starter motor.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips for diagnosing starter solenoid issues:
- No Click, No Start: If you turn the key and hear nothing (no clicking sound from the solenoid), check the following:
- Battery voltage: Ensure the battery is fully charged.
- Ignition switch: Verify that the ignition switch is functioning properly.
- Solenoid coil: Check for voltage at the solenoid's coil when the ignition key is in the "Start" position. If there's no voltage, the problem lies in the ignition switch circuit.
- Ground connection: Ensure the solenoid has a good ground connection. Clean and tighten the ground connection if necessary.
- Clicking Sound, No Start: If you hear a clicking sound from the solenoid but the starter motor doesn't crank, check the following:
- Battery voltage: Again, ensure the battery is fully charged. A weak battery can cause the solenoid to click but not provide enough current to the starter motor.
- Solenoid contacts: The contacts inside the solenoid may be corroded or damaged. You can try tapping the solenoid with a hammer (gently!) to see if it temporarily restores contact. This is a temporary fix; the solenoid likely needs to be replaced.
- Starter motor: The starter motor itself may be faulty.
- Battery Cable Connections: Important! Ensure that the battery connections at the terminals are tight and free of corrosion. Corrosion can greatly inhibit the amount of current supplied to the system.
- Starter Motor Cranks Slowly: This indicates a weak battery, poor connections, or a failing starter motor.
Testing the Solenoid: You can test the solenoid by bypassing it. Carefully use a heavy-gauge jumper cable to connect the battery's positive (+) terminal directly to the starter motor's positive (+) terminal. Use caution! If the starter motor cranks, the solenoid is likely faulty.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) battery cable to prevent accidental short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to avoid electric shock.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Batteries can release flammable gases.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from sparks and debris.
- Be Careful of Heat: The starter motor and solenoid can get very hot during operation. Avoid touching them immediately after use.
- High Current Danger: The battery and starter motor cables carry very high current. Never allow them to short circuit to ground. This can cause sparks, fires, and severe burns.
Specifically, the battery and starter motor cables are extremely risky. A short circuit in these areas can result in serious damage or injury. Be extra cautious when working with these components.
That was a thorough review of starter solenoid wiring diagrams. Remember that specific wiring diagrams can vary across models. To ensure accurate information, consult your ATV's service manual. We have a generic wiring diagram available for download to assist you further, and it can be downloaded from [Link to download]. Best of luck with your ATV adventures!
