Fuse Box Diagram For 1998 Honda Civic
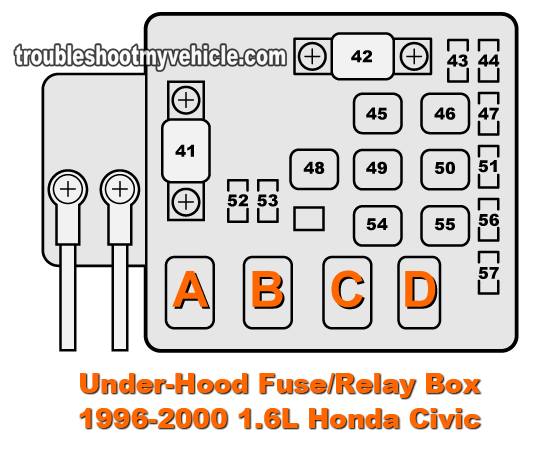
If you own a 1998 Honda Civic, you know it's a reliable machine. But even reliable cars need maintenance and repairs. One essential resource for keeping your Civic running smoothly is the fuse box diagram. This guide will walk you through understanding that diagram, enabling you to troubleshoot electrical issues, perform modifications, and generally better understand your car's electrical system. We'll break down the symbols, explain how it works, and give you some practical troubleshooting tips.
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
Why bother with a fuse box diagram? There are several key reasons:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: This is the primary reason. When an electrical component stops working – headlights, radio, power windows – the first place to check is the fuses. The diagram tells you which fuse corresponds to which circuit.
- Performing Modifications: Want to add aftermarket accessories like a new sound system or auxiliary lights? Understanding the fuse box layout allows you to tap into the electrical system safely and avoid overloading circuits.
- Preventing Electrical Fires: Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage is a recipe for disaster. The diagram tells you the correct amperage rating for each fuse, preventing overloads that can lead to electrical fires.
- General Understanding: Simply put, understanding the fuse box diagram gives you a better understanding of how your car's electrical system functions. This empowers you to perform basic maintenance and repairs yourself, saving you money and time.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 1998 Honda Civic Fuse Box
The 1998 Honda Civic typically has two fuse boxes:
- Under-Dash Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. This fuse box houses fuses for components like the interior lights, radio, power windows, and wipers.
- Under-Hood Fuse Box: Located in the engine compartment, this fuse box protects circuits for critical components like the headlights, engine control unit (ECU), fuel pump, and starter.
Inside each fuse box, you'll find:
- Fuses: These are the sacrificial components designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They are rated in amperes (amps), which indicates the maximum current they can handle before blowing. Common amperage ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 30A, and 40A. Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. For example, the headlight switch uses a relay to switch on the high-current headlights without requiring heavy-duty wiring to the switch itself.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool used to safely remove fuses. Never use pliers or other metal tools, as this can damage the fuse box or short out circuits.
- The Diagram Itself: Usually printed on a sticker located on the inside of the fuse box cover. This diagram is crucial for identifying which fuse controls which component.
Understanding the Symbols on the Fuse Box Diagram
Fuse box diagrams use a variety of symbols, lines, and colors to represent different components and connections. Here's a breakdown of common elements:
- Lines: Represent electrical wires or circuits. The thickness of the line doesn't typically indicate wire gauge in the diagram.
- Rectangles/Squares: Usually represent fuses. Next to the rectangle will be a number indicating the amperage rating of the fuse.
- Circles/Rounded Shapes: Often represent relays or other electrical components.
- Text Labels: The most important part! These labels describe what each fuse or relay protects. For example, "HEAD LP" would indicate a fuse for the headlights, and "FUEL PUMP" would indicate a fuse for the fuel pump. Abbreviations are common, so you might need to consult your owner's manual for a complete list.
- Colors (Sometimes): While not always present on every diagram, colors can sometimes be used to differentiate circuits or indicate voltage levels. For example, a red wire might indicate a constant 12V power supply.
It's important to note that the exact symbols and layout can vary slightly depending on the specific trim level and production year of your 1998 Civic. Always refer to the diagram that's specifically for your vehicle. Don't assume a diagram for a 1997 Civic is exactly the same as a 1998.
How It Works: The Fuse Box in Operation
The fuse box acts as a central distribution point and protection hub for your car's electrical system. Power from the battery flows through the fuse box, where it's distributed to various circuits, each protected by a fuse of the appropriate amperage rating.
Here's a simplified explanation of how a circuit works with a fuse:
- Power Source: The battery provides the electrical power.
- Wiring: Wires carry the electricity from the battery to the component.
- Fuse: The fuse is placed in the circuit to protect it. It's a thin wire or strip of metal designed to melt and break the circuit if the current exceeds its rated amperage.
- Component: The electrical component that's powered by the circuit (e.g., headlight, radio).
- Ground: The return path for the electricity back to the battery.
If there's a short circuit (e.g., a wire chafing against the metal chassis and creating a path to ground) or an overload (e.g., too many devices drawing power from the same circuit), the current flow will increase dramatically. This excessive current will cause the fuse to blow, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to the wiring and the electrical component.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram for basic troubleshooting:
- Identify the Problem: What electrical component isn't working?
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram and find the fuse that corresponds to the problematic component. For example, if your cigarette lighter isn't working, look for a fuse labeled "CIG LIGHTER" or something similar.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use the fuse puller to remove the fuse and visually inspect it. A blown fuse will typically have a broken filament (the thin wire inside). You can also use a multimeter to test the fuse for continuity. Set the multimeter to the continuity setting (usually indicated by a beep symbol) and touch the probes to each end of the fuse. A good fuse will beep, while a blown fuse will not.
- Replace the Fuse: If the fuse is blown, replace it with a new fuse of the exact same amperage rating.
- Test the Component: After replacing the fuse, test the component to see if it's working again.
- If the Fuse Blows Again: If the new fuse blows immediately or shortly after being replaced, there's a more serious problem in the circuit. This indicates a short circuit or an overload. Further investigation is needed, possibly involving tracing wires and checking for damaged components. In this case, it's best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Safety Considerations
Working with your car's electrical system can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some important safety tips:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on the fuse box or any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental short circuits and shocks.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage: This is the most important safety rule. Using a fuse with a higher amperage rating can overload the circuit and cause a fire.
- Be Careful Around High-Voltage Components: Some components, like the ignition system, operate at high voltages. Avoid touching these components while the engine is running.
- Use the Right Tools: Use the fuse puller to remove fuses. Don't use metal tools that could short out the circuit.
- Work in a Well-Lit Area: Good visibility is essential for safe and accurate work.
Warning: The components related to the airbag system are extremely sensitive and potentially dangerous. Mishandling can cause the airbags to deploy unexpectedly, resulting in serious injury. Unless you are specifically trained in airbag system repair, do not attempt to work on these components yourself. Consult a qualified mechanic.
Understanding your 1998 Honda Civic's fuse box diagram is a valuable skill for any car owner. It empowers you to troubleshoot electrical problems, perform modifications, and maintain your car's electrical system safely. Remember to always prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any aspect of the repair process. Happy wrenching!
We have the complete fuse box diagram file for the 1998 Honda Civic in a downloadable PDF format. Contact us and we will gladly provide it to you.
