Harness Hyundai Wiring Diagrams Free
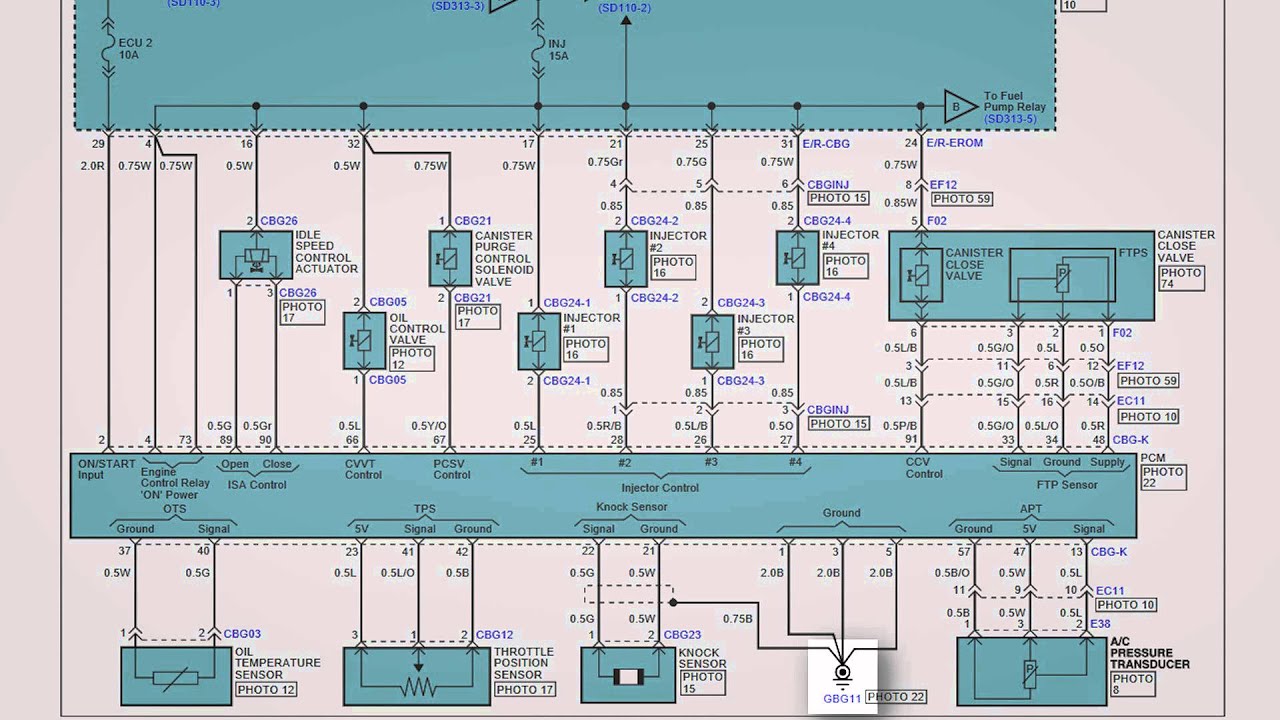
Okay, let's dive into Hyundai wiring diagrams. Specifically, how to find them for free, understand them, and use them effectively for diagnostics, repairs, or even customizing your ride. A good wiring diagram is indispensable, and having it for free is even better!
Purpose of a Hyundai Wiring Diagram
Why bother with a wiring diagram? Simple: electrical problems are often the most frustrating to diagnose because you can't see electricity. The wiring diagram provides a visual representation of the entire electrical system, allowing you to trace circuits, identify components, and pinpoint the source of a fault. Think of it as a roadmap for your car's electrical system.
Here's why you might need one:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: A blown fuse? Lights not working? The diagram helps you isolate the problem area.
- Performing Electrical Repairs: Replacing a sensor? Re-wiring a connector? The diagram shows you how everything connects.
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Adding a sound system, alarm, or auxiliary lighting? The diagram shows you where to tap into existing circuits safely.
- Understanding Vehicle Systems: Even if you're not currently experiencing a problem, studying the diagram can improve your overall understanding of how your Hyundai's systems function.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Wiring Diagram
Hyundai wiring diagrams, like most automotive diagrams, are schematic representations. They don't show the physical layout of the wiring harness, but rather the electrical relationships between components. Here are some key elements to understand:
- Power Source: Usually the battery, indicated by a symbol resembling a stack of plates or a capitalized 'B+' or 'BAT'. This is the starting point for many circuits.
- Ground: The return path for the electricity. Indicated by symbols that look like stacked triangles pointing downwards or the letters 'GND'. A good ground connection is crucial for proper operation.
- Fuses and Relays: Fuses are safety devices designed to break a circuit if the current exceeds a safe level. Relays are electrically operated switches that allow a small current to control a larger current. These are shown with specific symbols, usually squares or rectangles with internal markings.
- Switches: Devices that open or close a circuit, controlling the flow of electricity. Various switch types (toggle, rotary, push-button) are represented by different symbols.
- Loads: Components that consume electrical power, such as lights, motors, and sensors. These are also represented by specific symbols.
- Connectors: Where wires connect to components or other wires. Shown as interlocking shapes or circles. Understanding connector locations is critical for testing and repair.
- Wiring Harnesses: Bundles of wires that are grouped together and routed through the vehicle. The diagram often uses lines and shading to show how wires are grouped.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit) / ECM (Engine Control Module): The car's computer. Wiring diagrams will show which wires connect to the ECU/ECM and the pin numbers they connect to. This is vital for advanced diagnostics and troubleshooting.
Understanding Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Wiring diagrams use a standardized set of symbols and color codes. Understanding these is critical for interpreting the diagram correctly.
Lines:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line might, but doesn't always, indicate the wire gauge (thickness).
- Dashed Lines: Might represent shielded cables, control signals, or data buses (like CAN bus).
- Lines Crossing: If lines cross without a dot at the intersection, it usually means the wires are passing over each other and *not* connected.
- Lines Connected: If lines cross with a dot at the intersection, it indicates a wire splice or connection.
Color Codes:
Wire colors are usually indicated by abbreviations near the wire on the diagram. Here are some common examples:
- BK: Black
- RD: Red
- BL: Blue
- GN: Green
- WH: White
- YL: Yellow
- BR: Brown
- OR: Orange
Sometimes, you'll see two-letter codes, like LG (Light Green) or LB (Light Blue). And sometimes, a wire will have a stripe of another color, indicated by a slash. For example, WH/BK means a white wire with a black stripe.
Icons:
Icons represent components. While manufacturers use variations, there are common conventions:
- Resistors: Zigzag lines.
- Capacitors: Two parallel lines.
- Diodes: A triangle pointing towards a line.
- Inductors/Coils: Looped lines.
- Relays: A coil symbol connected to a switch symbol.
- Sensors: Varied, depending on the sensor type (e.g., temperature sensor, pressure sensor). Look for a symbol connected to a circle indicating the sensor element.
- Actuators: Also varied, depending on the actuator type (e.g., solenoid, motor).
How It Works: Tracing a Circuit
Let's say you're troubleshooting a non-working headlight. Here's how you'd use the wiring diagram:
- Identify the Headlight Circuit: Find the section of the diagram that covers the headlight system. This might be labeled "Headlights," "Exterior Lighting," or something similar.
- Locate the Power Source: Identify the wire that brings power to the headlight. This will typically be connected to a fuse and a switch (the headlight switch).
- Trace the Circuit: Follow the wire from the power source, through the fuse, through the switch, and to the headlight bulb.
- Identify Ground: Find the ground connection for the headlight. This will usually be a short wire connected to the vehicle's chassis.
- Test for Voltage: Using a multimeter, test for voltage at various points along the circuit. Start at the fuse and work your way towards the headlight. If you find voltage at the fuse but not at the headlight bulb, you know there's a break in the circuit somewhere in between.
- Check the Ground Connection: Ensure the ground connection is clean and secure. A poor ground can cause all sorts of electrical problems.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are a few practical tips for using wiring diagrams in your troubleshooting:
- Start with the Obvious: Check fuses first! A blown fuse is the most common cause of electrical problems. Use the wiring diagram to locate the correct fuse.
- Use a Multimeter: A multimeter is your best friend for electrical troubleshooting. Learn how to use it to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
- Test Ground Connections: Poor ground connections are a common cause of electrical issues. Clean and tighten any ground connections you find.
- Check Connectors: Inspect connectors for corrosion or loose pins. Clean and reseat any suspect connectors.
- Isolate the Problem: If you're working on a complex circuit, try to isolate the problem to a specific section of the circuit. This will make it easier to diagnose the issue.
- Don't Assume: Never assume anything when troubleshooting electrical problems. Always test and verify your assumptions with a multimeter.
Safety Considerations
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical system, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shorts.
- High Voltage Systems: Be extremely careful when working with components related to the ignition system (ignition coils, spark plugs) and especially with hybrid or electric vehicles. These systems can carry high voltages that can be lethal. Always discharge high-voltage systems according to the manufacturer's instructions before working on them.
- Airbag Systems: Airbag systems are explosive devices. Incorrect handling can cause them to deploy unexpectedly, resulting in serious injury. Consult the service manual for the proper procedures for disabling and servicing airbag systems.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Always wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks and debris.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to prevent electrical shock.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water is a conductor of electricity, so avoid working on electrical systems in wet conditions.
Disclaimer
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional advice. Always consult a qualified technician for complex electrical repairs.
Now, the good news! I can provide you with a Hyundai wiring diagram file. Just let me know the specific model and year of your Hyundai, and I'll do my best to locate a free diagram for you.
