Hei Ignition Chevy 350 Hei Distributor Wiring Diagram
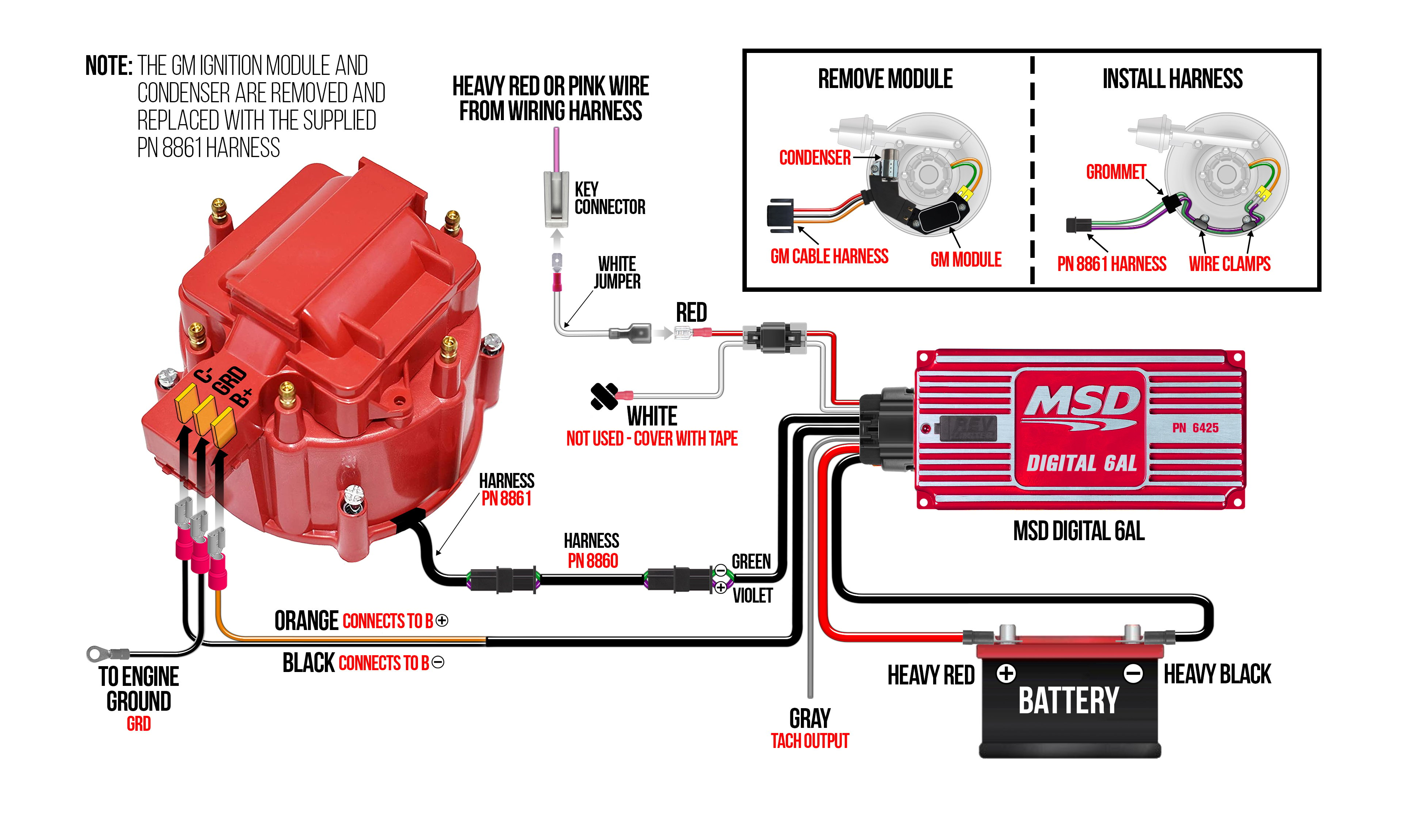
The High Energy Ignition (HEI) system, particularly on the Chevy 350 small-block engine, revolutionized automotive ignition by integrating most of the ignition components into a single, self-contained distributor. Understanding the HEI distributor wiring diagram is crucial for anyone maintaining, troubleshooting, or modifying these engines. Whether you're performing routine maintenance, diagnosing a no-start condition, or upgrading your ignition system, a clear grasp of the wiring is essential. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of the HEI wiring, helping you navigate the complexities with confidence.
Purpose of the HEI Wiring Diagram
The HEI wiring diagram serves several important purposes:
- Troubleshooting: Pinpointing the cause of ignition-related issues, such as a no-start condition, misfires, or weak spark.
- Repairs: Ensuring correct wiring when replacing components like the ignition module, pickup coil, or distributor cap.
- Upgrades/Modifications: Properly integrating the HEI distributor into different vehicles or adapting it for aftermarket performance enhancements.
- Understanding: Gaining a fundamental understanding of how the ignition system functions, empowering you to perform more advanced diagnostics and modifications.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before diving into the wiring diagram, it's important to understand the key components of the HEI distributor and their specifications.
- Distributor Housing: The main body of the distributor, containing and supporting the other components.
- Distributor Cap: The top cover of the distributor, routing the high-voltage spark to the correct spark plugs. Typically made of a durable plastic compound.
- Rotor: A rotating arm inside the distributor cap that directs the high-voltage spark from the coil to the correct terminal on the cap.
- Pickup Coil (Magnetic Pickup): A sensor that generates a signal when the distributor shaft rotates, triggering the ignition module to fire the coil. It's essentially a small coil of wire wrapped around a magnetic core.
- Ignition Module: An electronic switch that controls the primary current to the ignition coil, generating the high-voltage spark. The module receives a signal from the pickup coil.
- Ignition Coil: A transformer that steps up the battery voltage (typically 12V) to the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs (often 20,000-45,000 volts). In HEI systems, the coil is typically integrated into the distributor cap.
- Vacuum Advance Unit (Optional): A mechanism that advances the ignition timing based on engine vacuum, improving fuel economy and performance at part-throttle conditions.
- Mechanical Advance (Centrifugal Advance): A mechanism that advances the ignition timing based on engine speed (RPM), improving performance at higher RPMs. Uses weights and springs.
Key Specifications:
- Operating Voltage: 12V DC
- Spark Voltage: 20,000 - 45,000 volts (typically)
- Pickup Coil Resistance: Varies depending on the manufacturer, but typically ranges from 500-1500 ohms. Consult your specific HEI distributor's service manual.
- Coil Primary Resistance: Usually very low, often less than 1 ohm.
- Coil Secondary Resistance: Several thousand ohms (e.g., 6,000 - 10,000 ohms).
Symbols in the HEI Wiring Diagram
Understanding the symbols used in the wiring diagram is essential for interpreting it correctly. Typical symbols include:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires connecting different components. Thicker lines may indicate wires carrying higher current.
- Dashed Lines: Often used to represent ground connections or shielded wiring.
- Color Coding: Wires are typically color-coded to aid in identification. Common colors include Red (power), Black (ground), Brown (tachometer signal), and White or Yellow (trigger signals). Always refer to the specific diagram for your HEI setup, as color codes can vary slightly.
- Ground Symbol: Looks like an inverted triangle or a series of decreasing horizontal lines connected to ground (chassis).
- Connector Symbols: Indicate points where wires connect and disconnect, often represented by circles or rectangles with arrows.
- Component Symbols: Represent the different components of the HEI system, such as the coil, module, pickup coil, etc. These symbols are often simplified representations of the actual components.
Crucially, always refer to the specific wiring diagram for *your* particular HEI distributor. Variations exist depending on the manufacturer and model year.
How the HEI System Works
The HEI system's operation can be broken down into several key steps:
- Power Supply: The HEI system receives power from the vehicle's 12V electrical system, typically through a single, large-gauge wire connected directly to the battery or a reliable power source that is active when the ignition switch is in the 'Run' position. It is vital this wire provides a *full* 12V under load.
- Pickup Coil Signal: As the distributor shaft rotates, a reluctor (toothed wheel) passes by the pickup coil. This induces a small AC voltage signal in the pickup coil.
- Ignition Module Processing: The pickup coil signal is sent to the ignition module. The module interprets this signal as the correct time to fire the ignition coil.
- Coil Charging and Discharge: The ignition module controls the primary current flowing through the ignition coil. When the pickup coil signals, the module *interrupts* this current, causing the magnetic field in the coil to collapse rapidly.
- High-Voltage Generation: The rapid collapse of the magnetic field induces a very high voltage in the secondary winding of the ignition coil (the *step-up* transformer action).
- Spark Distribution: This high-voltage spark is directed to the correct spark plug by the rotor, which is synchronized with the engine's firing order.
- Spark Plug Firing: The high voltage jumps the gap at the spark plug, igniting the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some common troubleshooting scenarios and how the wiring diagram can help:
- No Spark: Use a test light or multimeter to check for power at the HEI distributor connector with the ignition on. If no power, trace the wiring back to the ignition switch and battery. If power is present, check the ground connection. Check the pickup coil resistance. If outside the specified range, replace the pickup coil. Consider replacing the ignition module – a common failure point.
- Weak Spark: Check the condition of the spark plugs, distributor cap, and rotor. Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage or corrosion. A weak coil can also cause this issue.
- Misfire: Check the spark plug wires for resistance and damage. A faulty distributor cap or rotor can also cause misfires. Use a timing light to verify the ignition timing is correct.
A common mistake is to assume the HEI system is receiving a full 12V. Voltage drop across old wiring is a frequent cause of problems. Use a multimeter to check voltage *at the distributor connector* while the engine is cranking.
Safety Precautions
The HEI system deals with very high voltages. Always take the following precautions:
- Disconnect the battery: Disconnect the negative battery cable before working on any part of the ignition system.
- Avoid contact with high-voltage components: Never touch the spark plug wires, distributor cap, or ignition coil while the engine is running or the ignition is switched on.
- Use insulated tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shock.
- Capacitor Discharge: Although not as common on HEI as with points-style ignition, be aware that capacitors within the system can store a charge even after the engine is turned off. It's best to let the system sit for a few minutes after disconnecting the battery before handling components.
The ignition coil and ignition module are particularly risky due to the high voltages involved. Handle these components with extreme caution.
Understanding the HEI distributor wiring diagram is essential for anyone working on Chevy 350 engines and other applications using this popular ignition system. By carefully studying the diagram and following the troubleshooting tips outlined above, you can confidently diagnose and repair ignition-related issues.
We have a downloadable version of a typical HEI Wiring Diagram available. Contact us, and we'll gladly send it to you.
