How To Wire A Starter Switch Diagram
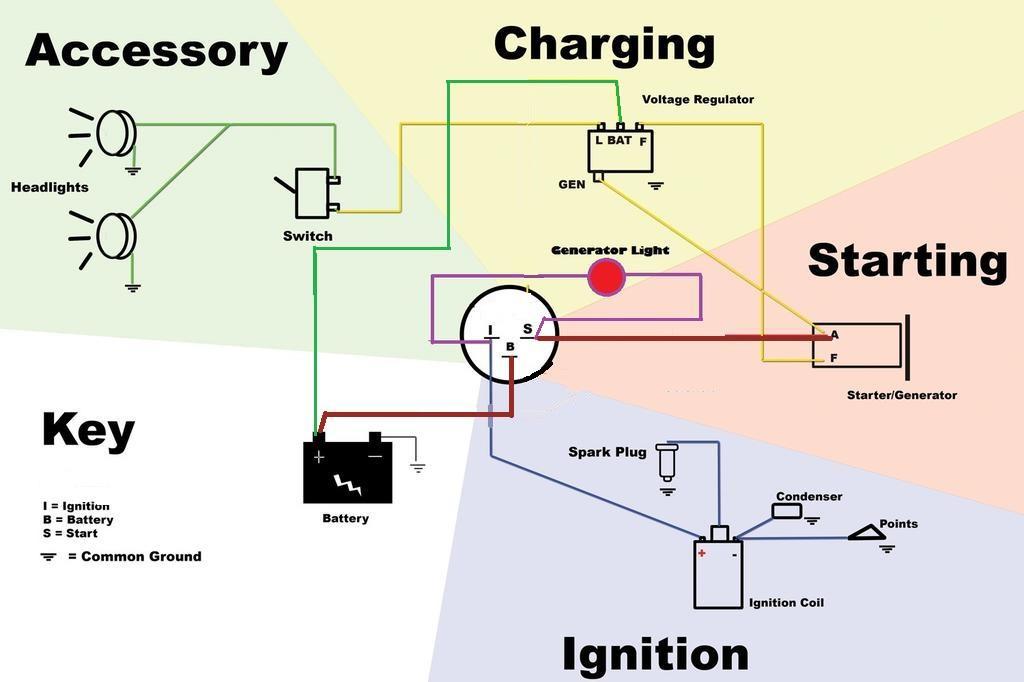
So, you're looking to dive into the world of starter switch wiring diagrams? Excellent! Whether you're troubleshooting a no-start condition, customizing your ride, or simply expanding your automotive know-how, understanding these diagrams is crucial. This article will break down everything you need to know, from the fundamental components to real-world application and safety considerations. We've also got a downloadable starter switch wiring diagram file for you to reference, which we'll mention again at the end.
Purpose: Why Master the Starter Switch Diagram?
Think of the starter switch diagram as the roadmap of your car's starting system. It's not just a nice-to-have; it's essential for:
- Troubleshooting Starting Issues: A diagram helps you trace the circuit, identify faulty components like a bad solenoid, relay, or even a corroded wire.
- Customization and Modification: Installing a new alarm system, remote starter, or even a push-button start requires understanding the existing wiring to avoid frying your system.
- Repair and Replacement: If you're replacing a faulty starter switch or related component, the diagram ensures you connect everything correctly.
- Education and Understanding: Even if you're not planning a project right now, understanding the diagram deepens your knowledge of how your car works, which is invaluable in the long run.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Starting Circuit
Before we jump into the diagram itself, let's define the key players in the starting system:
- Battery: The heart of the electrical system, providing the initial power needed to crank the engine. Pay attention to its voltage (typically 12V) and amp-hour (Ah) rating, which indicates its capacity.
- Ignition Switch (or Starter Switch): This is where you initiate the starting sequence. It has multiple positions: OFF, ACC (Accessory), ON (Run), and START. The START position activates the starter circuit.
- Starter Relay (or Solenoid): A heavy-duty switch that uses a small current from the ignition switch to control a larger current to the starter motor. This protects the ignition switch from high amperage loads.
- Starter Motor: The electrical motor that physically cranks the engine to initiate combustion. It requires a very high current to operate.
- Neutral Safety Switch (or Park/Neutral Position Switch): A safety device that prevents the engine from starting unless the transmission is in Park (P) or Neutral (N). This is crucial for preventing accidental starts.
- Wiring Harness: The network of wires that connects all the components. Pay attention to wire gauge (thickness), as it determines the current carrying capacity.
- Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Safety devices that protect the circuit from overcurrent. They are designed to blow or trip before damage occurs.
Decoding the Starter Switch Wiring Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
A wiring diagram is a schematic representation of the electrical circuit. Understanding the symbols is essential for interpreting the information it conveys:
- Lines: Represent wires. The thickness of the line doesn't necessarily indicate wire gauge in most simplified diagrams.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated by abbreviations (e.g., BLK for Black, RED for Red, BLU for Blue, GRN for Green, YEL for Yellow, WHT for White). A wire might be labeled "RED/WHT," meaning a red wire with a white stripe.
- Symbols:
- Battery: Depicted as a series of long and short parallel lines, indicating positive (+) and negative (-) terminals.
- Ignition Switch: A circle with lines extending from it, showing the different positions.
- Relay: A coil symbol (the electromagnet) and a switch symbol (the contacts).
- Starter Motor: A circle with an "M" inside, often with a gear attached.
- Neutral Safety Switch: A switch symbol, often with an indication of "P/N."
- Fuse: A squiggly line inside a rectangle.
- Ground: A symbol resembling an upside-down triangle or a series of lines getting shorter.
- Connectors: Represented by circles or squares where wires join.
- Abbreviations: Common abbreviations include:
- GND: Ground
- BAT: Battery
- IGN: Ignition
- ST: Starter
- ACC: Accessory
Pay close attention to the ground connections. A good ground is crucial for proper circuit operation. A bad ground can cause a variety of problems, from a weak starter to a completely non-functional system.
How the Starter Circuit Works
Here's a simplified explanation of how the starter circuit operates:
- Turning the Key: When you turn the ignition key to the START position, you send a small current to the starter relay's coil.
- Relay Activation: The current energizes the relay's coil, creating an electromagnetic field. This field pulls the relay's contacts together, closing the circuit.
- Power to the Starter Motor: Closing the relay contacts allows a large current from the battery to flow to the starter motor.
- Engine Cranking: The starter motor engages with the engine's flywheel or flexplate and cranks the engine.
- Engine Starts: Once the engine starts, you release the key, the current to the relay is cut, and the starter motor disengages.
The neutral safety switch is inline with the relay coil, only allowing current to flow when the transmission is in Park or Neutral. This prevents accidental starts.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say your car won't start. Here's how a wiring diagram can help:
- No Crank, No Start:
- Check the Battery: Is it fully charged? Use a multimeter to check the voltage.
- Check the Fuses: Consult the diagram to locate the fuse for the starter circuit. Replace any blown fuses.
- Check the Starter Relay: Can you hear it clicking when you turn the key to START? If not, it might be faulty. You can try swapping it with a known good relay (if you have one that's compatible).
- Check the Neutral Safety Switch: Try starting the car in both Park and Neutral. If it starts in one position but not the other, the neutral safety switch is likely the culprit.
- Check the Starter Motor: If all else fails, the starter motor itself might be bad. You can try tapping it with a hammer (gently!) while someone tries to start the car. If it starts, the starter motor needs to be replaced.
- Slow Cranking:
- Check the Battery: A weak battery can cause slow cranking.
- Check the Cables and Connections: Corroded or loose battery cables and connections can restrict current flow. Clean them thoroughly.
- Check the Starter Motor: A worn starter motor can also cause slow cranking.
Use a multimeter to check for voltage and continuity at different points in the circuit. This is the most effective way to pinpoint the location of a fault.
Safety First: Handle High-Current Components with Care
The starting circuit involves high currents, so safety is paramount:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery cable before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and shocks.
- Use Insulated Tools: Use tools with insulated handles to avoid electric shock.
- Wear Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from sparks and debris.
- Be Aware of Heat: Components like the starter motor can get very hot during operation. Avoid touching them immediately after use.
- Double-Check Connections: Ensure all connections are tight and secure. Loose connections can cause voltage drops and overheating.
Short circuits can cause fires and damage to your vehicle's electrical system. Always be careful when working with electrical wiring.
Understanding the starter switch wiring diagram empowers you to diagnose and repair starting issues, customize your vehicle, and gain a deeper understanding of automotive electrical systems. Remember to always prioritize safety and use the diagram as your guide.
And, as promised, we have a downloadable starter switch wiring diagram file available. It's a great resource to keep handy while you're working on your project. Let us know if you have any further questions!
