Ignition Switch Gm Steering Column Wiring Color Codes
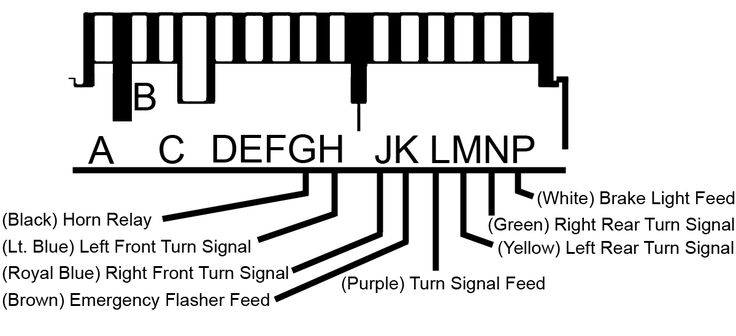
Understanding the ignition switch wiring in your GM steering column is crucial for various automotive tasks, from basic repairs and troubleshooting to more advanced modifications and security system installations. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to decoding the color codes and understanding the functionality of these wires, enabling you to diagnose problems accurately and perform repairs safely. We even have a downloadable diagram available for your reference!
Purpose of Understanding GM Ignition Switch Wiring
Why bother learning about these wires? The main reasons are:
- Troubleshooting: When your car won't start, the ignition switch is a prime suspect. Knowing the wiring allows you to test for voltage at different points, pinpointing the fault.
- Repair: Damaged or corroded wires need replacement. Accurate identification ensures you connect the correct wires to the correct terminals.
- Security System Installation: Many aftermarket security systems require tapping into specific ignition switch wires for features like remote start or anti-theft immobilization.
- Aftermarket ECU Installation: Advanced engine management systems may require connection to the ignition switch for proper power sequencing.
- Learning: Gaining a deeper understanding of your vehicle's electrical system empowers you to perform more complex repairs and modifications in the future.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the GM Ignition Switch System
Let's break down the core components and their functions:
- Ignition Switch: The primary control device, activated by the key. It’s a multi-position switch that connects different circuits based on the key's position (OFF, ACC, RUN, START).
- Ignition Cylinder: The mechanical component that receives the key and transmits the turning motion to the ignition switch.
- Steering Column: Houses the ignition switch, ignition cylinder, and related wiring. It also contains the locking mechanism that prevents steering when the ignition is off.
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connects the ignition switch to various electrical components, such as the starter solenoid, battery, and accessory circuits.
- Fuses: Essential safety devices that protect the electrical system from overloads. They are typically located in the fuse box and are crucial for diagnosing electrical problems.
Key Specs to consider:
- Voltage: Typically, the system operates on 12V DC.
- Wire Gauge: The thickness of the wires varies depending on the current they carry. Thicker wires are used for high-current circuits like the starter solenoid.
- Connector Types: GM uses various connector types, so it's important to identify the correct ones for your vehicle.
Decoding the Wiring Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
A wiring diagram is a schematic representation of the electrical system. Here's how to interpret the symbols and color codes:
- Lines: Solid lines represent wires. Dashed lines often indicate ground connections or shielded wiring.
- Colors: Each wire is identified by a unique color code. This is *critical* for correct identification. The most common colors are:
- Red: Typically indicates a constant 12V power source from the battery.
- Orange: Often represents accessory power.
- Yellow: Usually indicates power to the starter solenoid (engaged only during the START position).
- Pink: Often used for ignition power.
- Brown: Can be used for various circuits, often related to lighting or warning systems.
- Purple: Commonly associated with the starter solenoid circuit.
- Black: Always represents ground.
- Symbols:
- A circle with a line through it often symbolizes a ground connection.
- A rectangle with a line through it may represent a resistor.
- A zigzag line represents a coil (e.g., a relay coil).
Always refer to the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle's year, make, and model, as color codes can vary. The diagram we have available will be a helpful starting point.
How the GM Ignition Switch System Works
The ignition switch system works in a sequence, controlled by the key position:
- OFF: No circuits are energized. The engine is off, and most electrical accessories are disabled.
- ACC (Accessory): Some circuits are energized, allowing you to use the radio, windshield wipers, and other accessories without starting the engine. Orange wire is usually activated.
- RUN: The ignition system is powered up, and the engine control unit (ECU) receives power. The fuel pump is energized, and the engine is ready to start. Pink wire is generally hot here.
- START: The starter solenoid is energized, engaging the starter motor to crank the engine. Yellow wire provides power to the solenoid. This position is only active while the key is held in the START position. Once the engine starts, releasing the key returns it to the RUN position.
The ignition switch achieves this by internally connecting different sets of contacts based on the key position. Each contact corresponds to a specific wire and circuit. Understanding this sequence is key to diagnosing starting problems.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using your knowledge of the ignition switch wiring:
- No Start:
- Check the battery voltage. Ensure it's above 12V.
- Check the fuses related to the ignition system and starter. Replace any blown fuses.
- Test for voltage at the yellow wire when the key is in the START position. If there's no voltage, the ignition switch may be faulty, or there could be a wiring issue.
- Check the ground connection to the engine and chassis. A poor ground can prevent the starter from engaging.
- Engine Cranks but Doesn't Start:
- Check for voltage at the pink wire when the key is in the RUN position. If there's no voltage, the ECU may not be receiving power.
- Check the fuel pump relay and fuel pump fuse. The fuel pump needs to be energized to deliver fuel to the engine.
- Accessories Don't Work in ACC Position:
- Check the orange wire for voltage when the key is in the ACC position. If there's no voltage, the ignition switch may be faulty, or there could be a wiring issue.
- Check the fuses related to the accessory circuits.
Tools Needed: Multimeter, test light, wiring diagram, wire stripper, crimper, and connectors.
Safety Considerations: Highlighting Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shocks.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: When working with flammable liquids like fuel, ensure adequate ventilation to prevent fire hazards.
- Be Careful with Airbags: Some ignition switch circuits are related to the airbag system. Mishandling these circuits can cause the airbags to deploy, resulting in serious injury. If you're unsure, consult a qualified technician.
- Avoid Ground Loops: When adding new electrical components, ensure they are properly grounded to prevent ground loops, which can cause electrical noise and malfunctions.
The starter solenoid circuit carries a significant amount of current. Be extremely careful when working with this circuit, as a short can cause a fire.
By understanding the GM ignition switch wiring color codes and system functionality, you can confidently diagnose and repair electrical problems in your vehicle. Always refer to the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle and follow safety precautions to avoid injury or damage.
Ready to get started? We have the detailed GM steering column wiring diagram available for you. Understanding the color codes and wiring schematics will make your next project or repair easier and safer.
