Infiniti Q50 Serpentine Belt Diagram
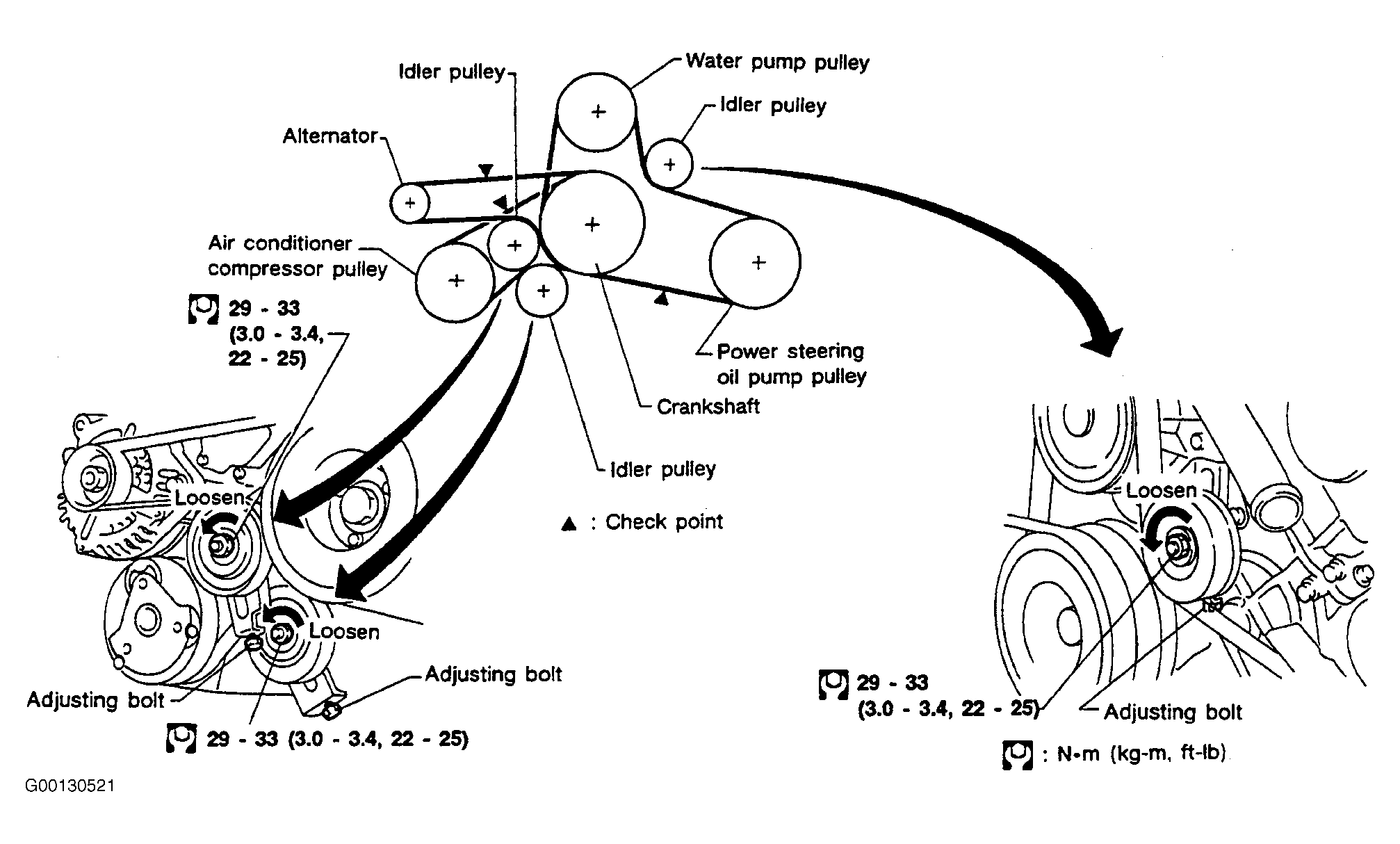
The serpentine belt, sometimes called a drive belt, is a critical component in your Infiniti Q50's engine. It's responsible for powering several vital accessories that keep your car running smoothly and comfortably. Understanding its layout and how it works is crucial for proper maintenance, troubleshooting, and even basic repairs. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the Q50's serpentine belt diagram, helping you navigate its complexities with confidence.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt diagram is essentially a roadmap for the belt's routing around various engine components. It serves several key purposes:
- Replacement Guide: If your belt is cracked, frayed, or showing signs of wear, the diagram shows you exactly how to route the new belt correctly. Incorrect routing can lead to serious damage to your engine and accessories.
- Troubleshooting Aid: A squealing or slipping belt can indicate a problem with one of the accessories it powers. The diagram helps you identify which component might be causing the issue.
- Educational Tool: Understanding the serpentine belt system provides valuable insight into your engine's operation and improves your overall car maintenance knowledge.
- Accessibility: Many engine bay stickers showing the belt diagram fade or disappear. Having a reliable digital copy ensures the information is always available.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The Infiniti Q50 serpentine belt drives the following components, though the exact configuration can vary slightly depending on the engine and year model (e.g., 2.0T, 3.0T, Hybrid):
- Crankshaft Pulley: The engine's crankshaft drives this pulley, which is the primary power source for the serpentine belt.
- Alternator: The alternator generates electricity to power your car's electrical system and charge the battery.
- Power Steering Pump: This pump provides hydraulic assistance to make steering easier.
- Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor: The compressor circulates refrigerant to cool the cabin air.
- Water Pump: The water pump circulates coolant through the engine to regulate its temperature. In some Q50 configurations, the water pump may be driven by a separate belt or internally driven. Refer to your specific diagram.
- Idler Pulley(s): These pulleys provide tension and guide the belt along its path. They don't drive any accessories.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley maintains proper belt tension. It's spring-loaded or hydraulically damped to automatically adjust for belt stretch and wear. A failing tensioner can lead to belt slippage and damage.
The belt length is a critical specification. Refer to your vehicle's service manual or a parts catalog to find the correct belt length for your specific model year and engine. Using the wrong belt length can cause improper tension and damage to the belt and accessories. Belts are typically constructed from a durable, ribbed rubber compound designed to withstand high temperatures and constant flexing. Some are reinforced with fibers for added strength.
Symbols and Conventions in the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Serpentine belt diagrams use specific symbols and conventions to represent the components and belt path. Understanding these is essential for accurate interpretation:
- Solid Lines: These represent the main path of the serpentine belt. The thickness of the line doesn't usually indicate anything other than visual clarity.
- Dotted Lines: Sometimes, dotted lines might indicate the location of pulleys or components hidden behind other parts. They can also represent the initial placement of the belt before tension is applied.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of belt rotation around each pulley. This is crucial for understanding how the belt drives the accessories.
- Component Icons: Simplified icons represent each component (alternator, power steering pump, etc.). These icons are typically labeled with abbreviations.
- Tensioner Arrow: This indicates the direction the tensioner moves to release tension on the belt. Always follow this direction when releasing the tensioner to avoid damaging it.
Colors are not commonly used on serpentine belt diagrams, however some diagrams may use color to highlight the front and back side of the belt run. If present, pay attention to what the color signifies in the legend of the diagram.
How It Works: The Serpentine Belt System
The serpentine belt system operates on a simple principle: the rotational force of the engine's crankshaft is transferred to various accessories via the belt. The crankshaft pulley spins the belt, which in turn drives the pulleys on the alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, and water pump. The tensioner pulley ensures the belt has enough grip on each pulley to prevent slippage.
The belt's grooved surface increases friction and gripping power. The tensioner is a critical component because it automatically adjusts for belt stretch and wear, maintaining optimal tension. Over time, the belt will stretch, and the tensioner will compensate by moving further along its travel range. Eventually, the tensioner will reach the end of its travel, and the belt will need to be replaced.
A slipping belt can cause a variety of problems, including a discharged battery (due to a non-charging alternator), loss of power steering, and lack of air conditioning. A broken belt will result in immediate failure of all driven accessories, potentially leading to overheating if the water pump is affected.
Real-World Use and Basic Troubleshooting
Here are some basic troubleshooting tips for your Q50's serpentine belt:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise, especially when the engine is cold or under load, often indicates a slipping belt. Check the belt for cracks, fraying, or glazing. Also, inspect the tensioner pulley for proper operation. A worn or damaged tensioner can cause the belt to slip.
- Cracked or Frayed Belt: Replace the belt immediately. A severely damaged belt can break without warning, leaving you stranded.
- Visible Wear: Check the belt for excessive wear, such as missing ribs or a shiny appearance. Replace the belt if you see any signs of significant wear.
- Accessory Malfunctions: If one of your accessories (e.g., alternator, power steering pump) is not working correctly, check the serpentine belt for proper tension and alignment. A loose or misaligned belt can prevent the accessory from functioning properly.
When replacing the serpentine belt, always follow these steps:
- Locate the tensioner pulley.
- Use a wrench or socket to rotate the tensioner pulley against its spring tension, relieving the tension on the belt.
- Remove the old belt.
- Route the new belt according to the diagram. Make sure the belt is properly seated in all the pulley grooves.
- Release the tensioner pulley, allowing it to apply tension to the new belt.
- Double-check the belt routing to ensure it is correct.
Safety Precautions
Working on the serpentine belt system can be risky. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any part of the engine, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent electrical shocks.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the serpentine belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any repairs.
- Moving Parts: Keep your hands and tools clear of moving parts when the engine is running. The serpentine belt and pulleys can cause serious injury.
- Tensioner Spring: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and can snap back forcefully if not handled carefully. Use the correct tool and technique to release the tension on the belt.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
The crankshaft pulley is spinning at engine speed. This means it poses an extreme danger if contacted while the engine is running. Do not attempt to remove the belt, diagnose issues, or make any adjustments while the engine is running.
We have a detailed serpentine belt diagram available for download for various Infiniti Q50 model years and engine types. This diagram provides a clear and accurate representation of the belt routing and component locations, making it an invaluable resource for maintenance and repairs. Please contact us through the 'contact us' form on this site to retrieve the files.
