International Truck Fuse Box Diagram
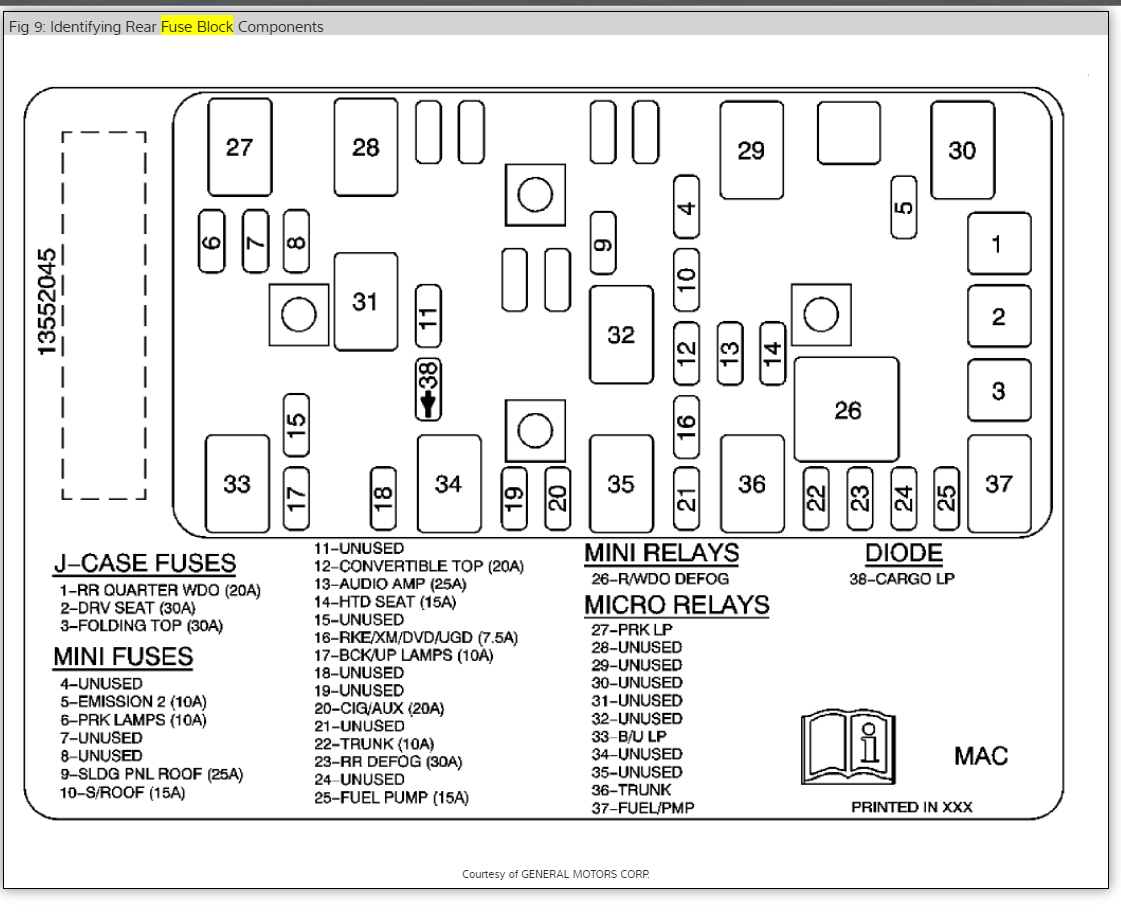
Hey folks, let's dive into something crucial for anyone who likes to tinker with their International truck: the fuse box diagram. Whether you're troubleshooting electrical gremlins, adding aftermarket accessories, or just trying to understand your truck's electrical system, having a solid understanding of the fuse box diagram is absolutely essential. Consider this your personal roadmap to electrical sanity.
Purpose – Why This Diagram Matters
So, why bother with a fuse box diagram? The simplest answer is prevention and repair. Fuses are designed to be the weak link in your electrical system, protecting vital components from overcurrent damage. When something goes wrong – a short circuit, a faulty component, or even just an overloaded circuit – a fuse blows, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing further damage. The fuse box diagram tells you which fuse protects which circuit. Without it, you're essentially working blind.
Beyond basic repairs, understanding the fuse box also empowers you to:
- Safely add aftermarket accessories: Want to install a new radio, auxiliary lights, or a power inverter? Knowing which circuits are available and their amperage rating is crucial for a safe and reliable installation.
- Diagnose electrical problems systematically: If a specific component isn't working, checking the corresponding fuse is the first and easiest step. The diagram guides you directly to the culprit.
- Gain a deeper understanding of your truck's electrical system: The diagram provides a visual representation of how different components are connected, improving your overall knowledge and troubleshooting skills.
- Avoid costly trips to the mechanic: Many common electrical issues can be resolved quickly and easily with a multimeter and the fuse box diagram.
Key Specs and Main Parts
The fuse box itself is typically located in one of several places: under the dashboard, in the engine compartment, or sometimes even in a side panel inside the cab. The exact location varies depending on the specific International truck model and year. The diagram is usually affixed to the inside of the fuse box cover, but if it's missing, you can often find it in the owner's manual or online (and, hint, we have one you can download later!).
Here's a breakdown of the key parts and specs to pay attention to:
- Fuse Locations: This is the heart of the diagram, showing the physical location of each fuse within the fuse box. They are often labeled with numbers or letters for easy identification.
- Fuse Amperage Rating: This is the maximum current (measured in amps, or "A") that the fuse can handle before blowing. Common amperage ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, and sometimes higher for heavy-duty circuits. Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating, as this can overload the circuit and cause serious damage or even a fire.
- Circuit Description: This describes what each fuse protects. For example, "Headlights," "Radio," "Windshield Wipers," "Fuel Pump," etc. This is crucial for identifying the correct fuse to check when troubleshooting.
- Relays: Some circuits also use relays, which are electrically operated switches that control higher-current circuits. The fuse box diagram will often indicate the location and function of these relays as well.
- Ground Points: While not directly on the fuse diagram, understanding where the main ground points are is vital for electrical troubleshooting. A poor ground connection can mimic the symptoms of a blown fuse.
Symbols – Explaining Lines, Colors, and Icons
Fuse box diagrams typically use a simplified visual language to convey information efficiently. Here's a breakdown of common symbols:
- Lines: Represent electrical wires. Thicker lines may indicate heavier gauge wires designed to carry more current.
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram using abbreviations (e.g., BLK for black, RED for red, GRN for green, YEL for yellow, BLU for blue, WHT for white). These colors are important for tracing wires and identifying specific circuits.
- Fuses: Usually represented by a small rectangle or square with the amperage rating inside.
- Relays: Typically shown as a small square or rectangle with a coil symbol inside, indicating the electromagnet that operates the switch.
- Ground Symbol: Represented by a series of descending lines, indicating a connection to the vehicle's chassis (ground).
- Component Icons: Simple icons may be used to represent the components being protected by the fuses (e.g., a headlight icon for the headlight fuse, a radio icon for the radio fuse).
It's important to note that the specific symbols and conventions may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer and model year, so always refer to the specific diagram for your International truck.
How It Works
Understanding the basic principles of how a fuse works is crucial for effective troubleshooting. A fuse contains a thin strip of metal that is designed to melt and break the circuit when the current exceeds a predetermined level. This protects the wiring and components connected to that circuit from overheating and potentially causing damage or a fire.
When a fuse blows, it's an indication that there's a problem somewhere in the circuit. The first step is to identify the circuit protected by that fuse using the fuse box diagram. Once you know which circuit is affected, you can begin to investigate the possible causes of the overcurrent condition. This may involve checking for short circuits (where a wire is accidentally contacting ground), faulty components, or overloaded circuits (where too many devices are drawing power from the same circuit).
Real-World Use – Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's a basic troubleshooting scenario:
- Symptom: Your headlights aren't working.
- Step 1: Consult the fuse box diagram to locate the fuse for the headlights.
- Step 2: Visually inspect the fuse. If the metal strip inside the fuse is broken or blackened, the fuse is blown.
- Step 3: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Step 4: Test the headlights to see if they now work.
- If the fuse blows again immediately: This indicates that there is a persistent problem in the headlight circuit, such as a short circuit or a faulty headlight bulb or wiring. Further investigation is required.
- If the headlights work after replacing the fuse: The problem is solved (at least temporarily). However, it's still a good idea to investigate the cause of the blown fuse to prevent it from happening again.
Remember to always use a multimeter to test for voltage and continuity when troubleshooting electrical problems. This will help you to identify the source of the problem more accurately and safely.
Safety – Highlight Risky Components
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are some important safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental shocks or short circuits.
- Use Insulated Tools: Always use tools with insulated handles when working on electrical circuits.
- Never Replace a Fuse with a Higher Amperage Rating: This can overload the circuit and cause serious damage or a fire.
- Be Careful Around the Airbag System: The airbag system is a complex and sensitive electrical system. Avoid working on or around the airbag system unless you are specifically trained to do so. Accidental deployment of an airbag can cause serious injury.
- When in doubt, consult a qualified mechanic: If you are not comfortable working on electrical systems, it's always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Components like the starter motor, alternator, and high-intensity discharge (HID) lighting systems operate at high voltages and currents, so exercise extra caution when working with these components.
So there you have it – a comprehensive overview of the International truck fuse box diagram. Hopefully, this has given you a better understanding of how to use this valuable tool to troubleshoot electrical problems and safely add aftermarket accessories to your truck. Remember safety first and don't hesitate to ask for help when needed.
And as promised, to get your copy of an International Truck Fuse Box Diagram, click this link. (Download and enjoy!)
