Metra Radio Interface Wiring Diagram
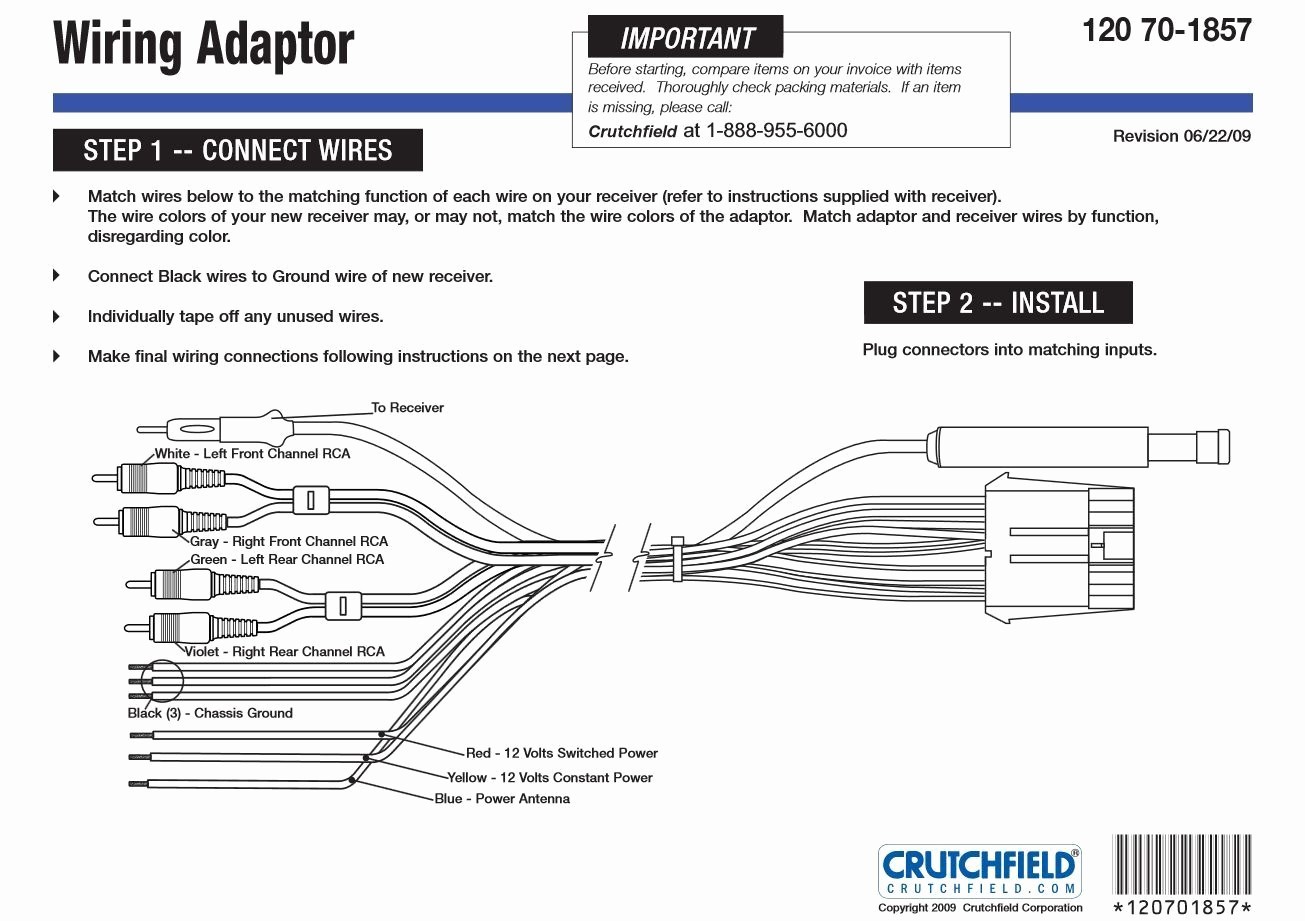
Alright, let's dive into the fascinating world of Metra radio interface wiring diagrams. Whether you're replacing a factory head unit, installing a new amplifier, or just trying to diagnose a pesky audio problem in your vehicle, understanding these diagrams is crucial. Think of it as the roadmap for your car's audio system. This isn't just for professionals; with a little patience and the right information, you can tackle many audio-related projects yourself.
Purpose: Decoding the Audio System's Language
Why bother with a wiring diagram? Simple: it's the key to understanding how all the components of your car's audio system are interconnected. Specifically, a Metra radio interface wiring diagram shows how a Metra interface module connects to your factory wiring harness and aftermarket radio. This is vital for several reasons:
- Radio Replacement: Installing an aftermarket radio in a car with a complex factory system often requires an interface to retain features like steering wheel controls, amplified systems, and factory navigation. The diagram shows exactly how to connect the Metra interface to both the car's wiring and the new radio.
- Troubleshooting: If your radio isn't working correctly, the diagram can help you trace the signal path and identify potential points of failure, such as a loose connection or a damaged wire.
- Learning: Even if you're not actively working on your car's audio system, studying the diagram can deepen your understanding of automotive electronics in general.
- Adding Aftermarket Components: If you want to add an amplifier, subwoofer, or other aftermarket components, the diagram can help you tap into the correct wires for power, ground, and signal.
Key Specs and Main Parts of a Metra Wiring Diagram
Before we dissect the diagram, let's familiarize ourselves with the main players and their specifications. A typical Metra radio interface wiring diagram will include representations of the following:
- Factory Wiring Harness: This is the connector that plugs into your factory radio. The diagram will show the color and function of each wire in this harness.
- Metra Interface Module: This is the "brain" of the operation, responsible for translating signals between your car's computer and the aftermarket radio. Different Metra modules cater to different vehicle makes, models, and features.
- Aftermarket Radio Connector: This is the connector that plugs into your new radio. It typically follows a standard pinout (more on that later).
- Speaker Wires: These wires connect the radio (or amplifier, if present) to the speakers.
- Power Wires: These provide power to the radio and interface module. Look for wires labeled "+12V," "Battery," and "Accessory."
- Ground Wires: These provide a return path for the electrical current. They're usually black and labeled "Ground" or "GND."
- Steering Wheel Control Wires: These wires allow you to control the radio using the buttons on your steering wheel (if equipped).
- Other Signals: Depending on the vehicle and the Metra interface, there may be wires for other signals, such as reverse trigger, parking brake, and illumination.
Understanding wire gauge is also essential. Wire gauge is denoted by the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard. Lower AWG numbers represent thicker wires that can carry more current. For example, a 12 AWG wire is thicker and can handle more amperage than a 18 AWG wire. Typically, power and ground wires will be thicker than signal wires.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
Wiring diagrams rely on a visual language to convey information concisely. Here's a breakdown of the common symbols you'll encounter:
- Lines: Lines represent wires. A solid line indicates a direct connection. A dashed line might indicate a shielded wire or a connection that's only present in certain configurations.
- Colors: Each wire is typically identified by a color code. Standard automotive wire colors include (but are not limited to) red, black, yellow, blue, green, white, gray, and brown. Often, the color will be abbreviated (e.g., "Red" or "RED" might be shortened to "R"). Some manufacturers use color codes with stripes (e.g., "Red/White" or "R/W").
- Connectors: Connectors are represented by various symbols, often resembling a plug or socket. The diagram will usually indicate the type of connector (e.g., a Molex connector) and the pin number of each wire.
- Ground Symbol: The ground symbol typically resembles a downward-pointing triangle or a series of horizontal lines diminishing in size.
- Component Symbols: While a wiring diagram primarily focuses on wires and connections, it may also include simplified symbols for components like the radio, amplifier, and speakers.
It is critical to remember that wire colors are *not* standardized across all manufacturers and models. Always rely on the diagram specific to *your* vehicle and interface.
How It Works: Signal Flow and Interface Logic
At its core, a Metra radio interface acts as a translator. Modern cars often have complex computer systems that integrate with the factory radio. These systems might use data buses (like CAN-bus) to transmit information such as volume control, track selection, and even vehicle diagnostics. When you replace the factory radio, you're essentially disconnecting the car's computer from this data stream.
The Metra interface intercepts these signals and translates them into a format that the aftermarket radio can understand. For example, when you press the "volume up" button on your steering wheel, the car's computer sends a signal over the CAN-bus. The Metra interface recognizes this signal and generates a corresponding signal that the aftermarket radio interprets as a volume increase. This signal goes through the Steering Wheel Control Wire, and goes to the back of the aftermarket radio. The radio can then increase the volume.
The module itself requires power and ground, like any electronic device. It usually gets +12V power from a constant (battery) source and an accessory (switched) source. The constant power keeps the module's memory alive, while the accessory power tells the module when the car is turned on.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Wiring diagrams are invaluable for troubleshooting. Here are a few common scenarios:
- No Power to Radio: Check the +12V and ground connections. Use a multimeter to verify that you're getting power to the radio and the interface module. Make sure the fuse for the radio circuit is intact.
- No Sound: Verify the speaker wire connections. Check the impedance of your speakers to ensure they are compatible with the radio or amplifier. If you have an amplifier, make sure it's receiving power and signal.
- Steering Wheel Controls Not Working: Double-check the steering wheel control wire connections. Some Metra interfaces require programming to learn the steering wheel control functions.
- Interference or Noise: Ensure that all ground connections are secure and properly grounded to the vehicle's chassis. Shielded cables can help reduce interference.
When troubleshooting, always start with the simplest solutions first. Visually inspect all connections for loose wires, corrosion, or damage. Use a multimeter to test for continuity and voltage. Refer to the wiring diagram to ensure that all connections are correct.
Safety First: Handling Risky Components
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. Here are a few safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on any electrical system. This will prevent accidental shorts and potential electrocution.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to avoid electrical shock.
- Protect Yourself: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: When soldering, work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Identify Airbags: Be aware of the location of airbags and avoid working near them unless you're properly trained. Accidental deployment of an airbag can cause serious injury.
Specifically, the +12V battery wire is a high-current circuit. If shorted to ground, it can cause a fire. Make sure to properly insulate all connections and use appropriately sized fuses.
By taking the time to understand the Metra radio interface wiring diagram, you'll be able to confidently tackle a wide range of audio-related projects. Remember to always double-check your work and prioritize safety.
We have the specific wiring diagram you're looking for. You can download the diagram from [hypothetical download link - replace with actual link]. Be sure to select the diagram that corresponds to your specific vehicle make, model, and year, as well as the specific Metra interface module you are using.
