Nissan 5 Wire Mass Air Flow Sensor Wiring Diagram
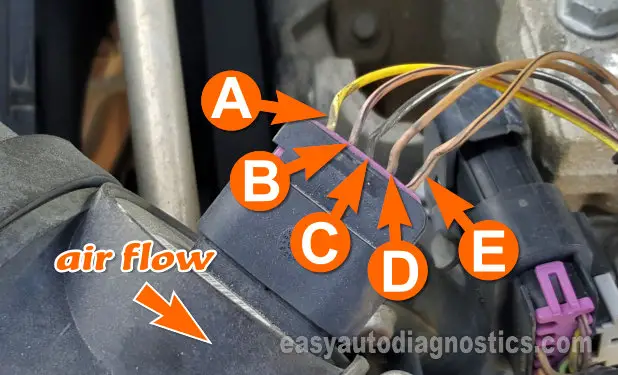
Alright, let's dive into the intricate world of Nissan's 5-wire Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor wiring diagram. If you're tackling engine performance issues, contemplating modifications, or just want a deeper understanding of your Nissan's engine management system, grasping this diagram is crucial. This isn't just a bunch of wires; it's the lifeline for accurate air-fuel mixture calculation, which directly impacts everything from fuel economy to horsepower.
Why This Diagram Matters
Having a solid understanding of the 5-wire MAF sensor wiring diagram unlocks a range of possibilities:
- Diagnosis and Repair: When your Nissan throws a code related to the MAF sensor (e.g., P0100, P0102, P0103), the diagram is your roadmap to pinpointing the problem. You can trace wires, check for voltage drops, and verify connections.
- Performance Tuning: For those venturing into engine modifications (intakes, exhaust systems), understanding the MAF sensor's readings and how they're interpreted by the ECU (Engine Control Unit) is essential for proper tuning. Altering the intake system, for example, can affect airflow, and you might need to adjust the MAF scaling.
- Upgrading/Swapping MAF Sensors: If you’re upgrading to a larger MAF sensor to accommodate more airflow (common in forced induction setups), you'll need the wiring diagram to ensure proper connection and signal interpretation by the ECU.
- Educational Purposes: Simply put, it's a great way to learn how your engine management system works. Knowing the purpose of each wire empowers you to become a more confident and competent DIYer.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dissect the diagram, let's cover the fundamental components:
- The MAF Sensor Housing: This is the physical unit that sits in the intake tract, typically between the air filter and the throttle body.
- The Sensing Element (Hot-Wire or Hot-Film): This is the heart of the sensor. It's a heated element that's cooled by the incoming airflow. The ECU monitors the current required to maintain a constant temperature, which is directly proportional to the mass of air flowing through it.
- The 5 Wires: This is where the diagram comes in. Each wire serves a specific purpose, usually power, ground, signal, and sometimes intake air temperature.
- ECU (Engine Control Unit): The brain of the operation. It receives the MAF sensor signal and uses it, along with other sensor inputs (throttle position, coolant temperature, etc.), to calculate the appropriate fuel injection duration and ignition timing.
A typical Nissan 5-wire MAF sensor wiring will include these wires:
- Power (12V or 5V): Supplies power to the sensor's electronics. This is usually a 12V or 5V source depending on the sensor type.
- Ground: Provides a return path for the electrical current. A good, clean ground is critical for accurate readings.
- MAF Signal: This wire carries the analog voltage signal representing the mass of air flowing through the sensor. The voltage typically increases as airflow increases.
- Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Signal: Many 5-wire MAF sensors integrate an IAT sensor. This wire transmits the IAT signal to the ECU, allowing it to compensate for air density variations.
- Ground (for IAT Sensor): Provides a ground for the integrated IAT sensor. Some diagrams will indicate a shared ground with the MAF sensor itself.
Symbols: Decoding the Diagram
Understanding the symbols in the wiring diagram is crucial. Here's a breakdown:
- Solid Lines: Represent wires. Thicker lines usually indicate wires carrying higher current.
- Dashed Lines: May indicate shielded wires or less critical connections.
- Color Codes: Wires are typically color-coded (e.g., Red/White, Blue/Black). The diagram will provide a key to decipher these colors. Always double-check the key!
- Connectors: Represented by squares, circles, or other shapes, with pins numbered or labeled. These show where wires connect.
- Ground Symbols: Indicate a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Resistors and Sensors: Represented by their standard electrical symbols (zigzag lines for resistors, specific symbols for temperature sensors).
The diagram will also show the wire routing, which is helpful for tracing wires and identifying potential damage. It depicts the physical path the wires take through the vehicle's wiring harness.
How It Works: The MAF Sensor in Action
Here's a simplified explanation of how the 5-wire MAF sensor functions:
- Airflow: Air enters the intake system and flows through the MAF sensor housing.
- Sensing Element: The airflow cools the heated sensing element (hot-wire or hot-film).
- Current Adjustment: The sensor's electronics adjust the electrical current flowing through the sensing element to maintain a constant temperature.
- Signal Generation: The current required to maintain that temperature is proportional to the mass of air flowing through the sensor. This current is converted into a voltage signal.
- ECU Input: The MAF sensor sends this voltage signal to the ECU via the MAF signal wire.
- Air Temperature Compensation: The integrated IAT sensor measures the temperature of the incoming air and sends this information to the ECU.
- Fuel Calculation: The ECU uses both the MAF signal (air mass) and the IAT signal (air temperature) to accurately calculate the amount of fuel to inject into the cylinders. This ensures the optimal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion.
Essentially, the MAF sensor is telling the ECU how much air is entering the engine, allowing it to precisely control the fuel mixture.
Real-World Use: Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some basic troubleshooting steps you can perform using the wiring diagram:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the MAF sensor connector and wiring for any signs of damage (corrosion, frayed wires, loose connections).
- Voltage Checks: Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage at the power wire. Refer to the diagram for the expected voltage (usually 12V or 5V). Also verify good ground connections.
- Signal Wire Test: With the engine running, use a multimeter to measure the voltage on the MAF signal wire. The voltage should change as you increase or decrease the engine's RPM. A steady, unchanging voltage indicates a potential problem.
- Continuity Tests: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of each wire between the MAF sensor connector and the ECU. This ensures that there are no breaks or shorts in the wiring.
- IAT Sensor Check: Use a scan tool to monitor the IAT sensor reading. Compare the reading to the ambient air temperature. A significantly different reading suggests a faulty IAT sensor or wiring issue.
- Scan Tool Data: Use a scan tool to monitor the MAF sensor readings (grams per second or lbs per minute). Compare these readings to the expected values for your engine and driving conditions.
Important Note: Always refer to your vehicle's specific repair manual for the correct voltage specifications and troubleshooting procedures. What works on one Nissan model might not apply to another.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Keep these safety precautions in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent accidental shorts or shocks.
- Be Careful with Wiring: Avoid cutting or splicing wires unless you are absolutely sure of what you are doing. Incorrect wiring can damage the ECU or other components.
- Use Proper Tools: Use a quality multimeter and wiring tools.
- Avoid Moisture: Keep electrical components dry. Moisture can cause shorts and corrosion.
- ECU Damage: The ECU is a very sensitive and expensive component. Always double-check your wiring before reconnecting the battery. Improper wiring can fry the ECU!
Working with the MAF sensor and its wiring requires careful attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the wiring diagram. By following these guidelines and taking the necessary safety precautions, you can successfully diagnose and repair MAF sensor issues, ultimately improving your Nissan's performance and fuel efficiency.
We have the complete Nissan 5-wire MAF sensor wiring diagram file available for download. This detailed resource will provide you with specific pinouts, color codes, and component locations for your vehicle. This detailed resource will provide you with specific pinouts, color codes, and component locations for your vehicle. This is a valuable asset for anyone working on their Nissan's engine management system.
