Nissan Rogue Serpentine Belt Diagram
The serpentine belt, also known as the accessory drive belt, is a crucial component in your Nissan Rogue's engine. It's responsible for powering several vital accessories that keep your vehicle running smoothly. Understanding its layout using a serpentine belt diagram is essential for maintenance, troubleshooting, and even some performance modifications. This article will provide a detailed breakdown of the Nissan Rogue's serpentine belt system, empowering you to confidently tackle related repairs and upgrades.
Purpose of the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Why bother with a diagram? Several reasons make it invaluable:
- Repair and Replacement: When replacing a worn or broken serpentine belt, the diagram is your guide to ensure the new belt is routed correctly. Incorrect routing can lead to accessory malfunction, belt damage, and even engine damage.
- Troubleshooting: Squealing noises, battery drain, overheating, or loss of power steering can often be traced back to a faulty serpentine belt or related components. The diagram helps you identify the belt's path and the accessories it drives, allowing for targeted diagnosis.
- Learning and Understanding: For the DIY mechanic, the diagram provides a visual representation of the engine's accessory drive system, fostering a deeper understanding of how everything works together.
- Preventative Maintenance: Periodically checking the belt's condition and tension is crucial. The diagram reminds you of the belt's layout and the location of the tensioner pulley.
- Modifications: If you're planning to upgrade an accessory like the alternator or power steering pump, knowing the serpentine belt routing is vital for ensuring proper belt length and fitment.
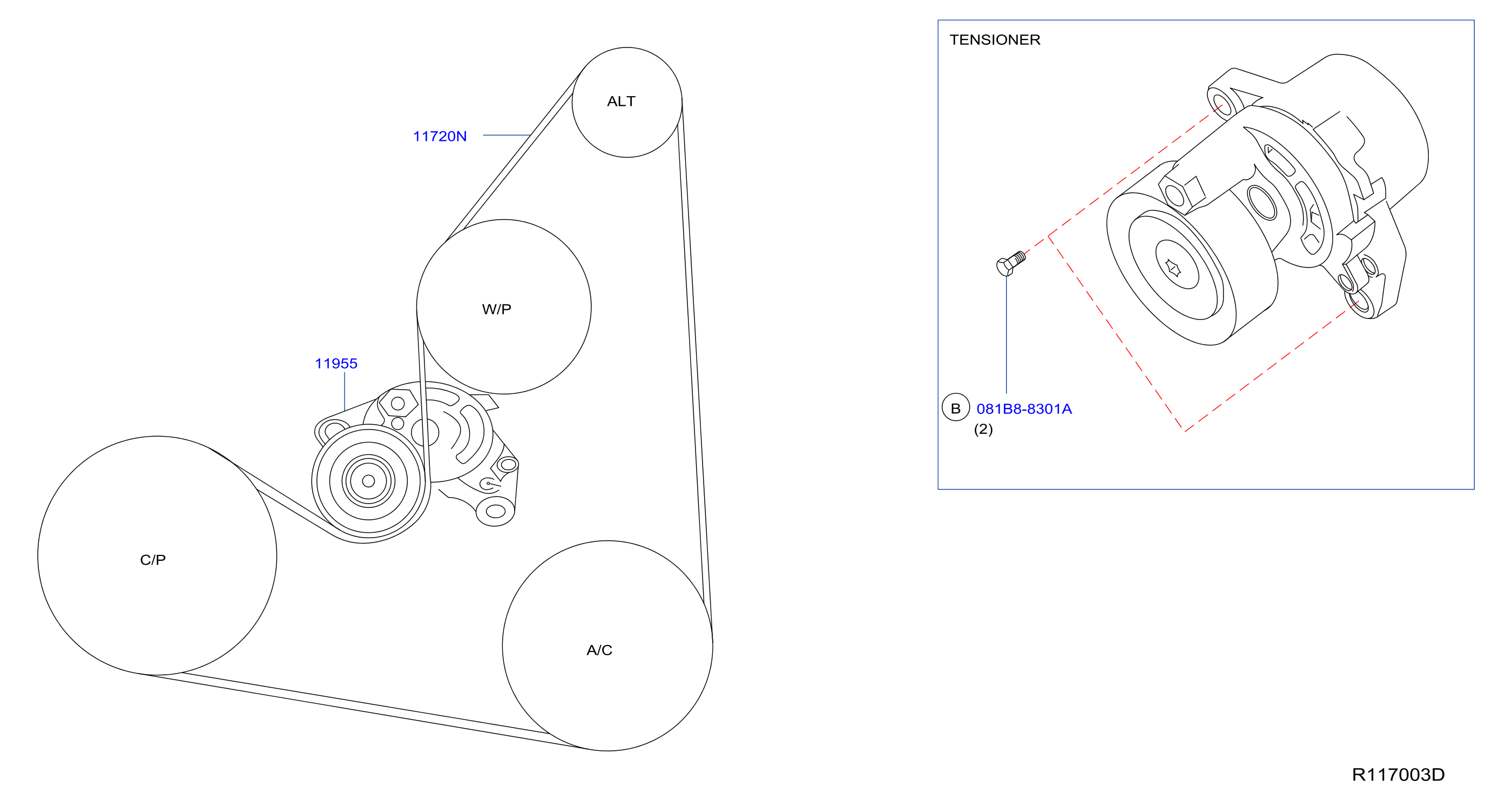
Key Specs and Main Parts of the Serpentine Belt System
The specific components and belt length can vary slightly depending on the Rogue's year and engine. However, the basic layout remains consistent. Here's a breakdown:
- Crankshaft Pulley: This pulley, connected to the engine's crankshaft, is the driving force behind the serpentine belt. Its rotation powers all the accessories connected to the belt.
- Alternator Pulley: The alternator, responsible for charging the battery and providing electrical power to the vehicle, is driven by the serpentine belt.
- Power Steering Pump Pulley: The power steering pump, which provides hydraulic assistance for easier steering, is also driven by the serpentine belt.
- Air Conditioning Compressor Pulley: The A/C compressor, responsible for cooling the cabin, is another accessory powered by the belt.
- Water Pump Pulley: In some Nissan Rogue configurations, the water pump (responsible for circulating coolant through the engine) is driven by the serpentine belt. This is less common in modern vehicles, with electric water pumps becoming more prevalent. Check your specific diagram to confirm.
- Tensioner Pulley: The tensioner pulley is spring-loaded and applies constant tension to the serpentine belt, preventing slippage and ensuring proper accessory operation. There are typically two types: manual and automatic. Automatic tensioners are more common on modern Rogues.
- Idler Pulley: An idler pulley is a smooth pulley that simply guides the belt around the engine. It helps to maintain proper belt routing and prevent interference.
- Serpentine Belt: The serpentine belt itself is a long, continuous belt made of durable rubber. Its ribbed design provides excellent grip on the pulleys. The length of the belt is critical and varies slightly between Rogue models and engine configurations. Always use the correct replacement belt specified for your vehicle.
Symbols and Conventions on the Serpentine Belt Diagram
Understanding the symbols on a serpentine belt diagram is crucial for interpreting its information. Here's a breakdown of common conventions:
- Solid Lines: Solid lines typically represent the path of the serpentine belt itself. Thicker lines may indicate the "outside" of the belt, while thinner lines might indicate the "inside."
- Dotted Lines: Dotted lines may represent the location of pulleys behind other components or highlight the direction of belt travel.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of rotation for each pulley. This is essential for ensuring the belt is routed correctly.
- Abbreviations: Common abbreviations include:
- ALT: Alternator
- P/S: Power Steering
- A/C: Air Conditioning Compressor
- W/P: Water Pump
- CRANK: Crankshaft
- TEN: Tensioner
- IDL: Idler
- Pulley Symbols: Pulleys are generally represented as circles. The symbol may include a representation of the ribs on the pulley, depending on the diagram's detail.
- Color Coding (Less Common): Some diagrams might use color coding to differentiate between sections of the belt or to highlight specific pulleys. Consult the diagram's legend for clarification.
How the Serpentine Belt System Works
The serpentine belt system is a relatively simple yet ingenious design. The engine's crankshaft, the source of power, rotates the crankshaft pulley. This rotation is transferred to the serpentine belt, which snakes its way around the various accessory pulleys. As the crankshaft pulley spins, it drives all the accessories connected to the belt, including the alternator, power steering pump, A/C compressor, and, in some cases, the water pump.
The tensioner pulley plays a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension. The spring-loaded mechanism constantly applies pressure to the belt, preventing slippage and ensuring that all accessories receive adequate power. Without proper tension, the belt can slip, causing accessories to malfunction and potentially damaging the belt itself.
The correct routing of the serpentine belt is absolutely critical. The belt must wrap around each pulley in the correct direction and with the proper amount of contact. Incorrect routing can lead to the belt rubbing against other components, incorrect accessory operation, and premature belt failure.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common problems and how the serpentine belt diagram can help:
- Squealing Noise: A squealing noise often indicates a loose or worn serpentine belt. Use the diagram to locate the tensioner pulley and check its condition. Also, inspect the belt for cracks, glazing, or missing ribs.
- Battery Drain: If your battery keeps dying, the alternator may not be charging properly. Use the diagram to confirm the serpentine belt is driving the alternator pulley effectively. A slipping belt can prevent the alternator from generating sufficient power.
- Overheating: If your Rogue is overheating, and it's using serpentine belt to drive water pump, ensure the belt is properly tensioned and driving the water pump pulley. If the pump isn't circulating coolant effectively, overheating can occur.
- Loss of Power Steering: If you experience difficulty steering, the power steering pump may not be functioning correctly. Check the serpentine belt and power steering pump pulley for proper operation.
- Visible Damage: Regularly inspect the serpentine belt for signs of wear and tear. Cracks, fraying, glazing, or missing ribs are all indicators that the belt needs to be replaced. Use the diagram to identify the belt's path and look for areas where it may be rubbing against other components.
Safety Considerations
Working on the serpentine belt system can be hazardous. Observe these safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on any electrical components, including the alternator. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Hot Engine: Never work on the serpentine belt system when the engine is hot. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any repairs.
- Moving Parts: Never put your hands or tools near the serpentine belt while the engine is running. The rotating belt and pulleys can cause serious injury.
- Proper Tools: Use the correct tools for the job, including a serpentine belt tool for releasing tension on the tensioner pulley.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Confined Spaces: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
The serpentine belt and its associated pulleys are located in a high-traffic area of the engine compartment. Exercise caution to avoid burns or cuts. The rotating components pose a significant risk of entanglement, so ensure the engine is off and the battery is disconnected before commencing any work.
We have a detailed serpentine belt diagram available for download. This diagram will provide you with a visual aid for understanding your Nissan Rogue's accessory drive system and will assist you in performing necessary maintenance and repairs.
