Nissan Sentra 2006 Fuse Box Diagram
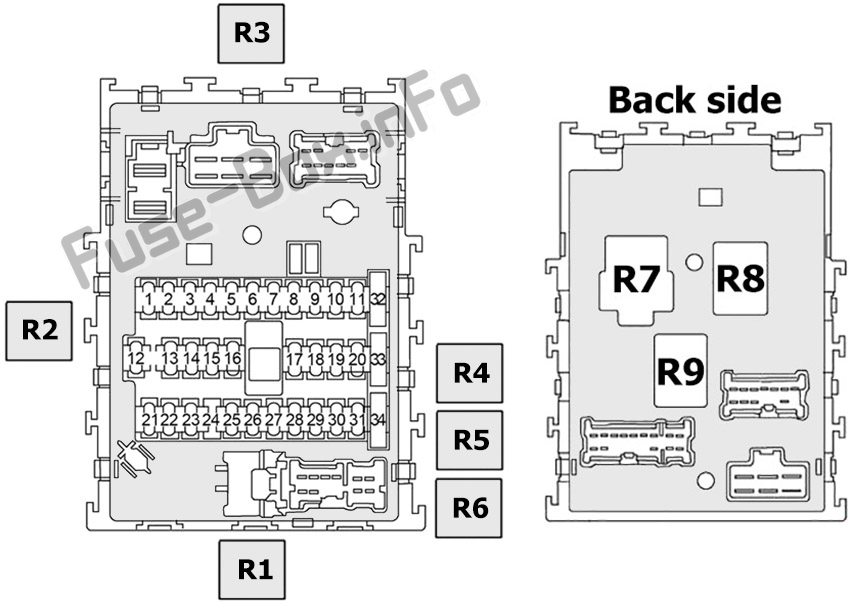
Alright, let's dive into the 2006 Nissan Sentra fuse box diagram. If you're a seasoned DIYer or even just an owner looking to get a deeper understanding of your car's electrical system, knowing your way around the fuse box is crucial. This isn't just about replacing a blown fuse; it's about diagnosing electrical problems, understanding circuit protection, and even safely tapping into the system for modifications.
Purpose: Why Bother With the Fuse Box Diagram?
The fuse box diagram is your roadmap to the car's electrical system. It serves several vital purposes:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Issues: When something electrical stops working (lights, radio, power windows, etc.), the fuse box is usually the first place to check. The diagram tells you which fuse protects which circuit.
- Identifying Circuits: Want to install a new accessory like a dashcam or aftermarket lights? Knowing which circuits are available and their amperage rating is essential for safe and reliable installation.
- Preventing Overloads and Fires: Fuses are designed to protect circuits from overcurrents. Replacing a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage can bypass this protection, potentially leading to overheating and even a fire. The diagram helps ensure you're using the correct amperage fuse.
- Understanding Your Car's Systems: Studying the diagram helps you understand how different electrical components are interconnected.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2006 Sentra Fuse Box
The 2006 Nissan Sentra typically has two main fuse boxes:
- Interior Fuse Box: Located inside the cabin, usually under the dashboard on the driver's side. This box houses fuses for interior components like the radio, lights, power windows, and other accessories.
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Located under the hood, this box contains fuses and relays for engine management systems, headlights, cooling fan, and other critical engine-related components.
Key specs to be aware of:
- Fuse Amperage Ratings: Fuses are rated in amps (A). Common ratings include 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A. Never replace a fuse with a higher amperage rating than specified on the diagram.
- Fuse Types: The 2006 Sentra likely uses blade-type fuses (also called spade fuses). These are small, rectangular fuses with two prongs that plug into the fuse box. There are different sizes of blade fuses, including standard, mini, and micro. Make sure you have the correct size for replacement.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-current circuits using a low-current signal. They are often used for components like the headlights, starter motor, and fuel pump.
Decoding the Symbols: Lines, Colors, and Icons
The fuse box diagram uses symbols to represent different components and circuits. Understanding these symbols is crucial for interpreting the diagram correctly.
- Lines: Lines represent electrical wires or connections between components. The thickness of the line may indicate the wire gauge (thicker lines usually indicate wires that can handle more current).
- Colors: Wire colors are often indicated on the diagram using abbreviations (e.g., BLU for blue, RED for red, GRN for green). These colors help you identify the correct wire in the vehicle.
- Icons: Icons represent specific components. Here are some common examples:
- Fuse Symbol: A zigzag line enclosed in a rectangle.
- Relay Symbol: A coil (representing the relay coil) and a switch (representing the relay contacts).
- Headlight Symbol: A stylized representation of a headlight.
- Horn Symbol: A stylized representation of a horn.
- Window Motor Symbol: A stylized representation of a motor driving a window.
The diagram will also include labels indicating the circuit that each fuse or relay protects. For example, a fuse might be labeled "Radio" or "Headlight (Left)".
How It Works: The Fundamentals of Circuit Protection
Fuses are sacrificial devices designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrents. When the current in a circuit exceeds the fuse's amperage rating, the fuse's internal element melts, breaking the circuit and preventing damage to other components. This is why it's crucial to use the correct amperage fuse. Using a fuse with a higher rating allows more current to flow, potentially damaging wires, components, and even causing a fire.
Relays, on the other hand, are used to control high-current circuits with a low-current signal. For example, the headlights require a significant amount of current. Instead of running that high current through the headlight switch, which could damage the switch, the switch activates a relay. The relay then closes, allowing the high current to flow directly from the battery to the headlights.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Let's say your radio suddenly stops working. Here's how you can use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot the problem:
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse box diagram for your 2006 Sentra. You can usually find it in the owner's manual or online. Identify the fuse that protects the radio circuit.
- Locate the Fuse: Open the relevant fuse box (likely the interior fuse box) and find the fuse corresponding to the radio.
- Inspect the Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse. If the internal element is broken or melted, the fuse is blown.
- Replace the Fuse: Replace the blown fuse with a new fuse of the same amperage rating.
- Test the Radio: Turn on the radio to see if it now works.
If the new fuse blows immediately, there's likely a short circuit in the radio circuit. This will require further investigation, potentially involving tracing wires and checking for damaged components. If the radio works but then the fuse blows again after a period of use, that could indicate a faulty radio drawing too much current.
Important Tip: Before replacing any fuse, turn off the ignition and any affected accessories. This reduces the risk of accidentally shorting the circuit during the replacement process.
Safety: Risky Components and Precautions
Working with electrical systems always carries some risk. Here are some key safety considerations:
- Battery Disconnection: If you're working on any major electrical repairs, consider disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery. This eliminates the risk of accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- High-Voltage Components: Be extremely cautious around components like the ignition system (especially the ignition coil), as they can generate high voltages that can be dangerous.
- Airbag System: The airbag system is electrically controlled and can be dangerous if mishandled. If you need to work near the airbag system, consult a qualified technician or refer to the service manual for proper procedures. Disconnecting the battery and waiting a specified time (usually 10-15 minutes) is often recommended to de-energize the system.
- Using the Correct Fuses: Never, ever replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. This can bypass the circuit protection and lead to serious damage or fire. Only use fuses that are specifically designed for automotive use and have the correct amperage rating.
- Wear Safety Glasses: When working with electrical components, wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from sparks or debris.
Warning: Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous if you're not careful. If you're not comfortable performing a particular task, it's always best to consult a qualified technician.
We have the full, high-resolution fuse box diagram for the 2006 Nissan Sentra available for download. This diagram will provide you with the detailed information you need to properly diagnose and repair electrical issues in your vehicle. It's in a user-friendly format, so you can easily print it out or view it on your computer or tablet. Get yours now and take control of your car's electrical system!
