Parts Of A Car Engine Diagram
So, you're ready to dive a little deeper into the heart of your car – the engine. Understanding an engine diagram isn't just about impressing your buddies at the next car meet; it's about empowering you to diagnose problems, perform maintenance, and even tackle some modifications with confidence. This article will break down the typical car engine diagram, explain its key components, and guide you on how to interpret its visual language. We've got a detailed diagram available for download too, which you can find at the end of this guide!
Why Bother with an Engine Diagram?
Let's be honest, engines are complex beasts. An engine diagram is like a roadmap, allowing you to visualize the internal workings and understand the relationships between various parts. More specifically, grasping the parts and their functions enables you to:
- Troubleshoot problems: When your car is acting up, a diagram can help you pinpoint the potential source of the issue.
- Perform maintenance: Regular maintenance, like replacing spark plugs or changing the oil, becomes much easier when you understand where everything is located.
- Plan modifications: If you're thinking about adding performance parts, a diagram helps you understand how those parts will interact with the rest of the engine.
- Learn and expand your knowledge: Ultimately, understanding engine diagrams is about becoming a more informed and capable car owner.
Key Specs and Main Parts: The Engine's Anatomy
An engine diagram will usually showcase some key specifications upfront, such as:
- Engine displacement: Measured in cubic centimeters (cc) or liters (L), this indicates the total volume swept by all pistons during a single stroke. Larger displacement often means more power.
- Engine configuration: Identifies the arrangement of cylinders (e.g., inline-4, V6, flat-6). Each configuration has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of balance, power delivery, and packaging.
- Firing order: The sequence in which the cylinders ignite. Knowing the firing order is crucial for certain diagnostic procedures.
- Compression ratio: The ratio of the volume of the cylinder when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke (Bottom Dead Center - BDC) to the volume when the piston is at the top of its stroke (Top Dead Center - TDC). A higher compression ratio usually results in more power, but also requires higher octane fuel.
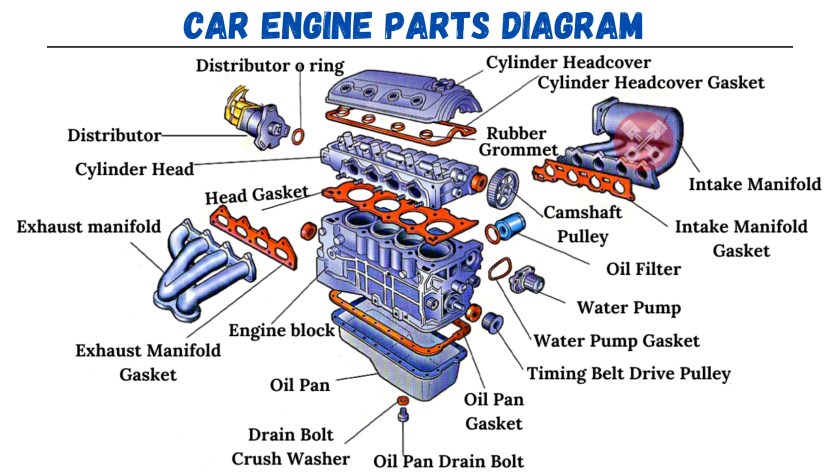
Now, let's dissect the main parts you'll find depicted in most engine diagrams. While specific layouts may vary depending on the engine type, these components are foundational:
Core Components
- Cylinder Block: The foundation of the engine, housing the cylinders. Often made of cast iron or aluminum.
- Cylinder Head: Sits atop the cylinder block, containing the valves, spark plugs (in gasoline engines), and combustion chambers.
- Pistons: Move up and down inside the cylinders, converting the energy from combustion into mechanical motion. Connected to the connecting rods.
- Connecting Rods: Connect the pistons to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: Converts the reciprocating (up-and-down) motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which drives the transmission.
- Valves: Control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders (intake valves) and the exhaust gases out (exhaust valves).
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the valves. Driven by the crankshaft, usually via a timing belt or chain.
- Spark Plugs: (Gasoline engines only) Ignite the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders.
Support Systems
- Intake Manifold: Distributes air to the cylinders.
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the cylinders.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the intake manifold or directly into the cylinders.
- Oil Pan: Reservoir for engine oil.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant through the engine to regulate temperature.
- Thermostat: Controls the flow of coolant to maintain optimal engine temperature.
- Distributor/Ignition Coils: (Depending on the engine type) Distribute or generate the high voltage needed to fire the spark plugs.
Decoding the Diagram: Symbols, Lines, and Colors
Engine diagrams use a standardized set of symbols to represent different components and their connections. Understanding these symbols is key to interpreting the diagram effectively:
- Solid Lines: Typically represent physical connections, such as hoses, pipes, or shafts.
- Dashed Lines: Often indicate control lines or vacuum lines.
- Arrows: Show the direction of flow (e.g., coolant, oil, air).
- Circles/Ovals: Can represent sensors, actuators, or other components. Look for labels or legends to identify their specific function.
- Color Coding: While not universally standardized, colors are frequently used to distinguish different systems. For example:
- Blue: Coolant system
- Red: Oil system
- Green: Fuel system
- Yellow: Electrical wiring
- Electrical Symbols: Resistors, capacitors, diodes, and other electrical components are represented by standard electronic symbols.
Diagrams may also use icons to represent specific components like the oil filter (a canister shape), the air filter (a rectangular box), or the battery (a stylized representation of a battery). Always refer to the diagram's legend to understand the meaning of any specific symbols or color codes used.
How It All Works: A Simplified View
While the diagram shows the layout of components, it's also beneficial to grasp the fundamental operation of the engine. In a nutshell:
- Intake: The piston moves down, drawing a mixture of air and fuel (in gasoline engines) or just air (in diesel engines) into the cylinder through the open intake valve.
- Compression: The piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture (or just air).
- Combustion: The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture (in gasoline engines), or fuel is injected into the hot compressed air (in diesel engines), causing an explosion that forces the piston down.
- Exhaust: The piston moves up, pushing the exhaust gases out of the cylinder through the open exhaust valve.
This four-stroke cycle repeats continuously, generating the power that drives the vehicle.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Now, let's put this knowledge to practical use. Here are some basic troubleshooting tips using the engine diagram:
- Overheating: Check the coolant hoses, radiator, water pump, and thermostat. The diagram will show you where these components are located. Look for leaks, cracks, or blockages.
- Oil Leaks: Refer to the diagram to identify potential leak sources, such as the oil pan, valve cover, or oil filter.
- Misfires: Use the diagram to locate the spark plugs and ignition coils. Check for damaged or worn-out components. Remember the firing order!
- Vacuum Leaks: Check vacuum lines for cracks or disconnections. The diagram will show you where these lines run. Vacuum leaks often lead to rough idling and poor performance.
Remember: Always consult your vehicle's specific repair manual for detailed troubleshooting procedures.
Safety First: Handle with Care
Working on your car engine can be rewarding, but it's essential to prioritize safety. Here are some key safety precautions:
- Disconnect the battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent shocks.
- Work in a well-ventilated area: Exhaust fumes and other chemicals can be harmful.
- Wear safety glasses: Protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Be careful with hot components: Allow the engine to cool down completely before working on it.
- Handle fuel carefully: Fuel is highly flammable. Avoid sparks and open flames.
- High-Pressure Fuel Lines: Be extremely cautious when disconnecting fuel lines, especially on fuel-injected engines. These lines are under high pressure, and fuel can spray out forcefully. Properly relieve pressure before disconnecting.
Crucially, certain components are best left to professionals. Modifying the ECU (Engine Control Unit), working on the fuel injection system, or opening up the engine block requires specialized knowledge and equipment. Know your limits!
With a clear understanding of engine diagrams and these safety considerations, you'll be well-equipped to tackle a variety of automotive projects. Now, as promised, you can download a detailed engine diagram right here. Good luck, and happy wrenching!
