Relay 2007 Nissan Murano Fuse Box Diagram
Let's dive into the 2007 Nissan Murano's fuse box and relay system. Understanding this electrical architecture is crucial whether you're tackling a minor electrical issue, installing aftermarket accessories, or simply wanting to gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle. This guide assumes you have some basic automotive knowledge and are comfortable working on your car.
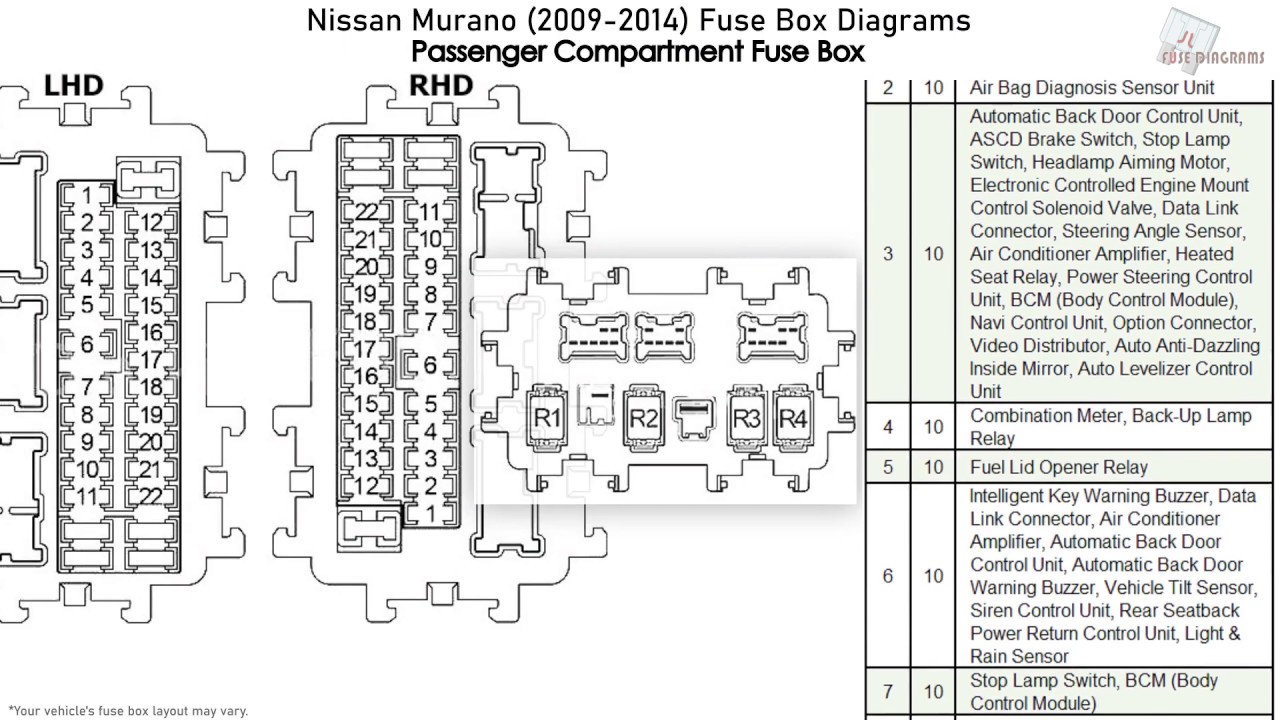
Purpose of the Fuse Box Diagram
A fuse box diagram is essentially a roadmap to your car's electrical system. It details the location of each fuse and relay, along with the specific circuits they protect or control. Without it, you're flying blind. The diagram is vital for:
- Troubleshooting Electrical Problems: Identifying blown fuses is the first step in diagnosing many electrical faults. The diagram tells you exactly which fuse corresponds to which circuit (e.g., headlights, radio, power windows).
- Installing Aftermarket Accessories: Properly tapping into the electrical system for adding things like lights, sound systems, or remote starters requires knowing where to draw power safely and which circuits to avoid overloading.
- Learning Vehicle Systems: Studying the diagram gives you insights into how different components are powered and interconnected, which can be extremely helpful in understanding the overall vehicle operation.
- Preventing Further Damage: Replacing a blown fuse with the correct amperage prevents potential damage to the wiring and connected components. Using the wrong fuse can be catastrophic.
Key Specs and Main Parts of the 2007 Murano Fuse System
The 2007 Nissan Murano, like most modern vehicles, has multiple fuse boxes. The two primary locations are:
- Interior Fuse Box: Usually located under the dashboard, often on the driver's side. This box typically houses fuses for interior systems like the radio, power windows, interior lights, and the cigarette lighter (power outlet).
- Engine Compartment Fuse Box: Situated in the engine bay, usually near the battery. This box protects circuits related to engine management, headlights, cooling fans, and other critical vehicle functions.
Key components found within these fuse boxes include:
- Fuses: These are safety devices designed to protect circuits from overcurrent. They contain a thin wire that melts and breaks the circuit if the current exceeds a certain limit. Fuses are rated in amperes (amps or A), indicating the maximum current they can handle. Common types include blade fuses (ATO, Mini, Micro2) and cartridge fuses.
- Relays: Relays are electromechanical switches that allow a low-current circuit to control a high-current circuit. They're used to switch on/off things like headlights, fuel pumps, and starter motors. A relay typically consists of a coil, a set of contacts (normally open or normally closed), and an armature. When the coil is energized, it creates a magnetic field that moves the armature, switching the contacts.
- Fuse Puller: A small plastic tool used to safely remove fuses from the fuse box. Avoid using metal objects like screwdrivers, as this can damage the fuse box or cause a short circuit.
- Spare Fuses: Most fuse boxes include a few spare fuses of different amperage ratings. These are invaluable for quick repairs.
Understanding Fuse Box Diagram Symbols
Fuse box diagrams use a standardized set of symbols to represent different components and connections. Deciphering these symbols is key to using the diagram effectively.
- Lines: Lines represent wires connecting different components. Different colors might be used to indicate wire gauge or circuit function. However, the diagram itself rarely dictates the wire color in the car's harness.
- Fuse Symbol: Typically shown as a rectangle with a squiggly line inside. The amperage rating is usually printed next to the symbol.
- Relay Symbol: Usually shown as a square or rectangle, with the relay coil and contacts depicted schematically. The diagram might indicate the relay's function (e.g., headlight relay, fuel pump relay).
- Ground Symbol: Indicates a connection to the vehicle's chassis ground.
- Connectors: Represented by circles or rectangles. These indicate points where wires can be disconnected.
- Color Codes: While the diagram generally does not show wire colors, some diagrams might use abbreviations like "BLU" for blue, "RED" for red, "BLK" for black, etc., next to wire lines, but rely on an external wire diagram for accuracy.
It's crucial to consult the specific diagram for your 2007 Nissan Murano, as there might be slight variations depending on the vehicle's trim level and options. A diagram may have a legend section, explaining any unique symbols or abbreviations used.
How It Works: The Electrical Flow
The basic principle is simple: electricity flows from the battery, through the fuses and relays, to the various components in your car. The fuse protects the circuit from overcurrent by interrupting the flow if the current exceeds the fuse's rating. The relay allows a low-current switch (like a headlight switch) to control a high-current circuit (like the headlights themselves).
For example, consider the headlights. When you turn on the headlight switch, a small current flows through the relay coil. This energizes the coil, causing the relay contacts to close. This allows a much larger current to flow from the battery, through the headlight fuses, and to the headlights, turning them on. If there's a short circuit in the headlight wiring, the current will surge, blowing the headlight fuse and protecting the rest of the electrical system. Understanding that fuses are a critical safety component will help you not to bypass them to test.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here's how to use the fuse box diagram to troubleshoot common electrical problems:
- Identify the Problem: Determine which system is malfunctioning (e.g., the radio doesn't work, the headlights are out).
- Consult the Diagram: Locate the fuse or relay associated with the malfunctioning system in the fuse box diagram.
- Inspect the Fuse: Use a fuse puller to remove the fuse. Visually inspect it for a broken filament. You can also use a multimeter to check for continuity. If the fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse of the same amperage rating. Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating, as this could damage the circuit.
- Check the Relay: If the fuse is good, the problem might be with the relay. Relays can fail due to coil burnout or contact wear. Swapping the relay with a known-good relay (of the same type) is a common troubleshooting step. If swapping the relay fixes the problem, replace the faulty relay.
- Further Investigation: If replacing the fuse or relay doesn't solve the problem, there might be a wiring issue or a faulty component. At this point, you might need to consult a more detailed wiring diagram or seek professional help.
Example: Your interior lights suddenly stop working. You consult the fuse box diagram and find the fuse labeled "Interior Lights." You remove the fuse and see that the filament is broken. You replace the fuse with a new one of the same amperage. The interior lights now work.
Safety Precautions
Working with automotive electrical systems can be dangerous. Keep these safety tips in mind:
- Disconnect the Battery: Before working on any electrical components, disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery. This will prevent accidental short circuits and electrical shocks.
- Use the Right Tools: Use a fuse puller to remove fuses. Avoid using metal objects like screwdrivers, as this can cause short circuits or damage the fuse box.
- Never Bypass a Fuse: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or other conductive material. This can cause a fire or serious damage to the electrical system.
- Be Careful with High-Voltage Components: Some components, like the ignition system and the alternator, operate at high voltage. Avoid touching these components with the engine running.
- Know Your Limits: If you're not comfortable working on electrical systems, seek professional help.
The battery and the alternator are especially risky. The battery can output large amounts of current, and the alternator is running high-voltage electrical components.
By understanding the fuse box diagram and following proper safety procedures, you can confidently tackle many electrical repairs and modifications on your 2007 Nissan Murano. Remember that you are working on the life-blood of your car, electricity, and safety should always be the number one priority.
We have a downloadable version of the 2007 Nissan Murano fuse box diagram available. This diagram will provide you with a detailed visual guide to the fuse and relay locations, as well as their corresponding circuits. Please reach out to us if you need to download the file. Good luck!
