Toyota Tacoma Exhaust System Diagram
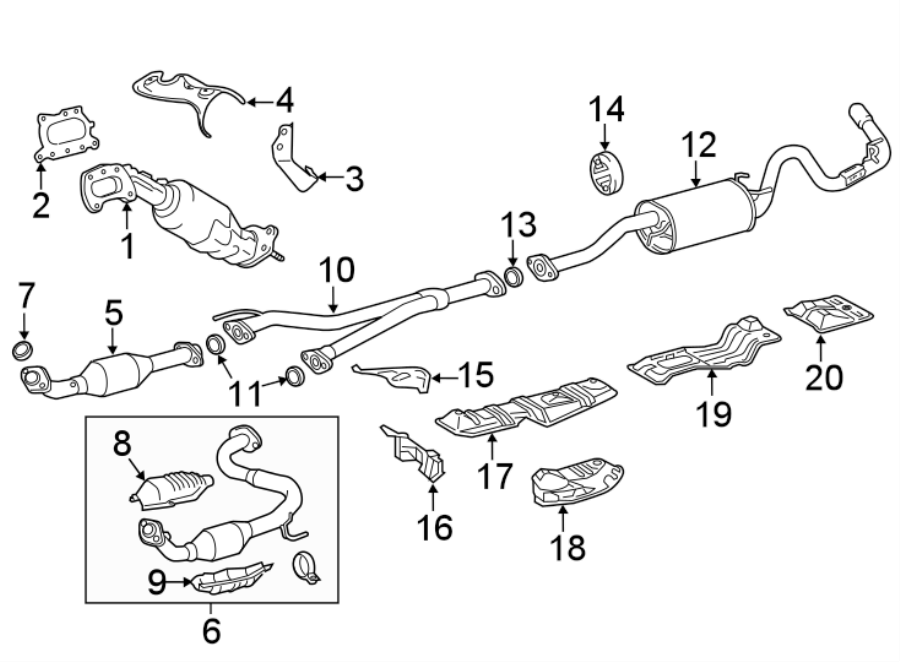
The exhaust system on your Toyota Tacoma is more than just a way to get rid of fumes; it's a carefully engineered system that plays a crucial role in your truck's performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Understanding its layout and components is invaluable for diagnosing problems, performing repairs, and even making informed decisions about aftermarket modifications. That’s where the exhaust system diagram comes in. This detailed schematic gives you a visual roadmap of the entire system, from the engine manifold to the tailpipe.
Purpose of the Toyota Tacoma Exhaust System Diagram
Why bother with an exhaust system diagram? Simple. It provides a visual aid that simplifies complex systems. Here's how it helps:
- Troubleshooting: Pinpointing the exact location of a leak, rattle, or other issue becomes much easier when you can trace the system visually.
- Repairs: The diagram helps you understand how components connect, making removal and installation processes smoother.
- Modifications: Planning upgrades like installing a new muffler or catalytic converter requires a clear understanding of the existing system layout.
- General Knowledge: Even if you're not actively working on your exhaust, understanding its components and function enhances your overall automotive knowledge.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before diving into the diagram itself, let's familiarize ourselves with the key components of a typical Tacoma exhaust system:
- Exhaust Manifold(s): Attached directly to the engine cylinder head(s), the manifold collects exhaust gases from each cylinder. Tacomas, depending on the engine (e.g., 2.7L inline-4 or 3.5L V6), will have either one or two manifolds. The manifold is usually made of cast iron or stainless steel.
- Catalytic Converter(s): A crucial emissions control device that uses catalysts to convert harmful pollutants (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides) into less harmful substances. Modern Tacomas typically have one or two catalytic converters, sometimes even more complex setups in California emissions compliant models.
- Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors): These sensors monitor the oxygen content of the exhaust gas, providing feedback to the engine control unit (ECU) for optimal air-fuel mixture control. You'll typically find one or more O2 sensors upstream (before) the catalytic converter and one or more downstream (after) the converter.
- Exhaust Pipe(s): These pipes connect the various components of the exhaust system. They are typically made of aluminized steel or stainless steel.
- Muffler: The muffler reduces noise generated by the engine's exhaust pulses. It uses internal chambers and baffling to dampen sound waves.
- Resonator (Optional): Some Tacomas have a resonator, which further reduces noise and drone. It is typically located between the catalytic converter and the muffler.
- Tailpipe: The final section of the exhaust system, which directs exhaust gases away from the vehicle.
- Hangers and Mounts: Rubber or metal hangers that secure the exhaust system to the vehicle's undercarriage, preventing it from vibrating and damaging other components.
- Flanges and Gaskets: These connect the different sections of the exhaust system and create a seal to prevent leaks.
Understanding Symbols in the Exhaust System Diagram
The diagram uses a standardized set of symbols and conventions to represent different components and their connections. Here's a breakdown:
- Lines: Solid lines typically represent exhaust pipes. Dotted or dashed lines might indicate vacuum lines, electrical connections, or other related systems. The thickness of the line can sometimes indicate the pipe diameter.
- Colors: While not always present, color coding can highlight different sections or materials. For example, the catalytic converter might be shaded a different color to distinguish it from the pipes.
- Component Icons: Each component has a specific icon. A catalytic converter is often represented by a rectangular box with internal partitions. Mufflers are usually depicted as cylindrical shapes. Oxygen sensors might be shown as small circles with electrical connections.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction of exhaust gas flow.
- Abbreviations: Common abbreviations include "CAT" for catalytic converter, "O2S" for oxygen sensor, "MAN" for manifold, and "MUF" for muffler.
- Numerical Labels: Numbers are often used to identify specific parts or connection points. These numbers may correspond to part numbers in a parts catalog.
It's crucial to consult the legend or key that accompanies the diagram. This legend will provide specific explanations for the symbols and colors used in that particular diagram.
How the Tacoma Exhaust System Works
The exhaust system’s job is to remove spent gases from the engine’s combustion chambers and expel them safely into the atmosphere. Here’s the process:
- Exhaust Stroke: During the exhaust stroke of the engine cycle, the exhaust valve opens, and the piston pushes the burned gases out of the cylinder.
- Manifold Collection: The exhaust gases flow into the exhaust manifold, which collects the gases from all cylinders and channels them into a single or dual exhaust pipe(s).
- Catalytic Conversion: The gases then pass through the catalytic converter(s), where harmful pollutants are chemically converted into less harmful substances.
- Oxygen Sensor Feedback: Oxygen sensors monitor the exhaust gas composition before and after the catalytic converter. The upstream sensor(s) provide feedback to the ECU for air-fuel mixture adjustments, while the downstream sensor(s) monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
- Noise Reduction: The exhaust gases then flow through the muffler and resonator (if equipped) to reduce noise.
- Final Exhaust: Finally, the gases exit the vehicle through the tailpipe.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting
The exhaust system diagram is your best friend when troubleshooting. Here are some examples:
- Exhaust Leak: If you hear a hissing or puffing sound, use the diagram to visually inspect the exhaust system for cracks, holes, or loose connections, starting from the manifold and working your way back. Pay close attention to flanges and welds.
- Rattling Noise: A rattling sound could indicate a loose heat shield, a broken hanger, or internal damage to the muffler or catalytic converter. The diagram helps you identify these components and their mounting points.
- Check Engine Light (CEL): If the CEL is on, the code reader may indicate a problem with the O2 sensors or catalytic converter. The diagram shows you the location of these sensors, making it easier to inspect them. If you see a code related to catalyst efficiency (like P0420), knowing where your catalytic converter is located is essential.
Example: Let's say you have a P0137 code indicating a low voltage from O2 Sensor 2 (Bank 1). Using the diagram, you can quickly locate the downstream O2 sensor on the passenger side (assuming it's a V6 Tacoma). You can then inspect the sensor for damage, check its wiring, and test its voltage with a multimeter.
Safety Considerations
Working on an exhaust system can be hazardous. Here are some safety tips:
- Heat: Exhaust components get extremely hot. Always allow the system to cool completely before working on it. Burns are a serious risk.
- Lifting: Use jack stands to support the vehicle securely before working underneath it. Never rely solely on a jack.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris and rust.
- Breathing Protection: Wear a respirator or dust mask when working with exhaust components, as they can contain harmful particles.
- Catalytic Converters: Never tamper with or remove catalytic converters unless you are replacing them with a compliant unit. Removing them is illegal in many jurisdictions and can result in fines.
- Penetrating Oil: Use penetrating oil to loosen rusted bolts and fasteners.
- Welding: If welding is required, take appropriate safety precautions, including wearing a welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing. Disconnect the vehicle's battery to prevent electrical damage.
Important Note: The catalytic converter is one of the riskiest components. It operates at high temperatures and contains precious metals that are highly valuable to thieves. Protect your vehicle by parking in well-lit areas and considering aftermarket anti-theft devices.
Understanding your Tacoma's exhaust system is key to keeping it running efficiently and legally. With the right diagram and a bit of know-how, you can tackle many exhaust-related repairs and modifications yourself. Always remember to prioritize safety and consult a qualified mechanic if you're unsure about any aspect of the job.
We have a detailed Toyota Tacoma exhaust system diagram available for download. This diagram will provide you with a clear and comprehensive view of your truck's exhaust system, helping you to diagnose problems, plan repairs, and make informed decisions about modifications. This is the same type of diagram that would be included in a service manual.
