Windshield Wiper 5 Wire Wiper Motor Wiring Diagram
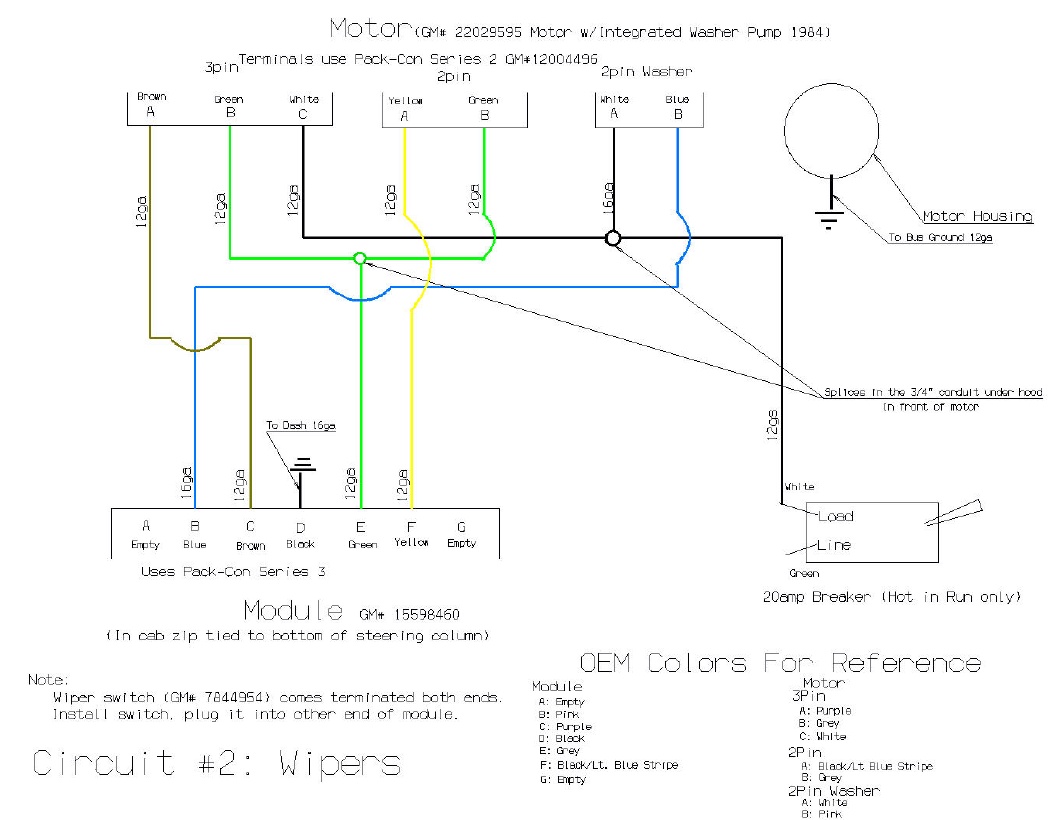
So, you're diving into the world of windshield wiper motors – specifically the 5-wire variety. Good on you! Understanding how these systems work is crucial whether you're troubleshooting a faulty wiper, attempting a custom installation, or simply expanding your automotive knowledge. This guide will break down the 5-wire wiper motor wiring diagram, giving you the confidence to tackle most wiper-related challenges. We've got the actual diagram file ready for you to download later in this article. This isn't just about fixing a squeaky wiper; it's about understanding a fundamental electrical system in your vehicle.
Purpose of the Wiring Diagram
Why bother with a wiring diagram? Well, imagine trying to rewire your house without knowing where the wires go. Chaos, right? The wiring diagram serves as a roadmap for your windshield wiper system. It's essential for:
- Troubleshooting: Identifying faulty wiring, shorts, or open circuits.
- Repairs: Replacing a motor, switch, or damaged wiring.
- Custom Installations: Modifying your wiper system for a different motor or adding features.
- Understanding System Operation: Grasping how the various components interact to provide the desired wiper functions.
Without the diagram, you're essentially guessing, which can lead to incorrect connections, damage to components, and frustration. A proper diagram allows you to work systematically and efficiently.
Key Specs and Main Parts
Before we dive into the diagram itself, let's familiarize ourselves with the key specifications and components of a 5-wire wiper motor system:
- Wiper Motor: The heart of the system, converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to move the wiper arms. These are typically 12V DC motors.
- Wiper Switch: Controls the motor's operation, selecting different speeds and modes (low, high, intermittent, off).
- Wiring Harness: A bundle of wires that connect all the components.
- Linkage: Mechanical arms that connect the motor to the wiper arms, translating the motor's rotary motion into the back-and-forth movement of the wipers.
- Park Switch (Internal to Motor): This is a critical component inside the motor. It ensures the wipers return to their "parked" position when switched off. This function requires specific wiring configurations.
The "5-wire" designation refers to the number of wires connecting to the motor. These wires provide the necessary power, ground, speed control, and park functionality. Key specifications include voltage (usually 12V DC), current draw (which can vary depending on the motor size and load), and motor torque (the rotational force the motor can produce).
Symbols and Diagram Conventions
Understanding the symbols and conventions used in the wiring diagram is crucial for accurate interpretation. Here are some common elements:
- Lines: Represent wires. Solid lines indicate direct connections. Dashed lines may indicate connections through a relay or switch.
- Colors: Wires are typically color-coded (e.g., Red for power, Black for ground, Blue for low speed). Consult the specific diagram for your vehicle or motor, as color codes can vary.
- Ground Symbol: Usually represented by three downward-pointing lines, indicating a connection to the chassis ground.
- Motor Symbol: Often shown as a circle with an "M" inside.
- Switch Symbol: Depicts the switch's internal contacts and how they change position when the switch is toggled.
- Resistor Symbol: A zig-zag line, representing a resistor used for speed control.
- Relay Symbol: A coil and a switch, indicating an electrically operated switch.
The diagram will also indicate wire gauge (thickness), which is important for ensuring adequate current carrying capacity. Thicker wires are used for higher current circuits. Pay close attention to the legend or key provided with the diagram, as it will define the specific symbols and color codes used.
How It Works: The 5-Wire System
The 5 wires on a typical wiper motor perform the following functions:
- Power (12V+): Supplies the main power to the motor. Often directly from the ignition switch or through a relay.
- Ground: Provides the return path for the electrical current.
- Low Speed: Activates the motor at its low-speed setting. This may involve a resistor to reduce the voltage applied to the motor.
- High Speed: Activates the motor at its high-speed setting, bypassing any resistors.
- Park: This is the most crucial and unique wire. It's connected to an internal switch within the motor that is mechanically linked to the motor's rotating shaft. This switch maintains power to the motor even after the main wiper switch is turned off, until the wipers reach the "parked" position. Then, the internal switch opens, cutting power and stopping the motor. This function ensures the wipers don't stop mid-cycle.
When you select a different speed on the wiper switch, you are essentially directing power to different wires on the motor. The "Park" wire is always connected when the ignition is on, but its functionality is only relevant when the wipers are turned off.
Real-World Use: Basic Troubleshooting Tips
Here are some common wiper problems and how the wiring diagram can help you troubleshoot them:
- Wipers Don't Work at All: Check the power wire for voltage with a multimeter. Also, confirm a good ground connection. Use the diagram to trace the circuit back to the power source and the switch. A blown fuse is a common culprit.
- Wipers Only Work on High Speed: The low-speed circuit may be faulty. Use the diagram to trace the low-speed wire and check for continuity. The resistor in the low-speed circuit could be burned out.
- Wipers Don't Park: This is often a problem with the park switch or the "Park" wire. Check the continuity of the "Park" wire and ensure the internal park switch is functioning correctly. Replacing the motor might be necessary.
- Wipers Work Erratically: This could be due to loose connections, corroded terminals, or a faulty switch. Use the diagram to inspect all connections in the wiper circuit.
Remember to use a multimeter to check for voltage, continuity, and resistance. A test light can also be helpful for checking for power and ground.
Safety Considerations
Working with electrical systems can be dangerous. Here are some safety precautions:
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal of the battery before working on any electrical system. This prevents accidental shorts and electrical shocks.
- Use Proper Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent shocks.
- Avoid Working in Wet Conditions: Water conducts electricity, increasing the risk of shock.
- Be Careful with Relays: Relays can contain capacitors that store electrical charge even after the power is disconnected. Discharge the capacitor before handling the relay.
- Fuses Protect Your Vehicle: Never bypass a fuse with a wire or a higher amperage fuse. Doing so can lead to a fire. Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage.
The wiper motor itself, while not carrying extremely high voltage, can still deliver enough current to cause a shock, especially if wiring is damaged or exposed. Always exercise caution.
We have prepared a sample 5-wire wiper motor wiring diagram file for you. You can download it here. Remember to consult the specific wiring diagram for your vehicle or motor, as wiring configurations can vary.
